Neuroimmune Mechanisms Underlying Neuropathic Pain: The Potential Role of TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway
- PMID: 35806192
- PMCID: PMC9266916
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23137191
Neuroimmune Mechanisms Underlying Neuropathic Pain: The Potential Role of TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway
Abstract
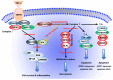
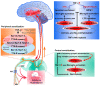
The neuroimmune mechanism underlying neuropathic pain has been extensively studied. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a key pro-inflammatory cytokine that drives cytokine storm and stimulates a cascade of other cytokines in pain-related pathways, induces and modulates neuropathic pain by facilitating peripheral (primary afferents) and central (spinal cord) sensitization. Functionally, TNF-α controls the balance between cell survival and death by inducing an inflammatory response and two programmed cell death mechanisms (apoptosis and necroptosis). Necroptosis, a novel form of programmed cell death, is receiving increasing attraction and may trigger neuroinflammation to promote neuropathic pain. Chronic pain is often accompanied by adverse pain-associated emotional reactions and cognitive disorders. Overproduction of TNF-α in supraspinal structures such as the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and hippocampus plays an important role in pain-associated emotional disorders and memory deficits and also participates in the modulation of pain transduction. At present, studies reporting on the role of the TNF-α-necroptosis pathway in pain-related disorders are lacking. This review indicates the important research prospects of this pathway in pain modulation based on its role in anxiety, depression and memory deficits associated with other neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, we have summarized studies related to the underlying mechanisms of neuropathic pain mediated by TNF-α and discussed the role of the TNF-α-necroptosis pathway in detail, which may represent an avenue for future therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: necroptosis; neuroinflammation; neuropathic pain; tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 22;24(20):15454. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015454. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895135 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the anterior cingulate cortex contributes to neuropathic pain and pain-associated aversion.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Oct;130:104456. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31028871
-
Neuroinflammation in the anterior cingulate cortex: the potential supraspinal mechanism underlying the mirror-image pain following motor fiber injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jun 20;19(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02525-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35725625 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of proinflammatory factors TNF-α,IL-1β, IL-6 on neuropathic pain].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Oct;42(19):3709-3712. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170907.004. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29235283 Review. Chinese.
-
The kiss of (cell) death: can venom-induced immune response contribute to dermal necrosis following arthropod envenomations?Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019 Aug;57(8):677-685. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1578367. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 30806093 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and disulfidptosis co-regulate neuronal cell in neuropathic pain based on bioinformatics analysis.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241290114. doi: 10.1177/17448069241290114. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 39323309 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Natural Product-Derived Compounds on Inflammatory Pain via Regulation of Microglial Activation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;16(7):941. doi: 10.3390/ph16070941. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37513853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 22;24(20):15454. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015454. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895135 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain, antidepressant drugs, and inflammation: a narrative review.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 Sep 27;4(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00204-z. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39334307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Mean Platelet Volume Combined with Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting the Therapeutic Effect of Splanchnic Neurolysis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Oct 31;16:5027-5037. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S428641. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37927957 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

