ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- PMID: 35799597
- PMCID: PMC9202073
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2022-0484
ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
Abstract
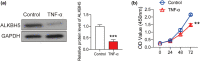
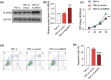
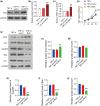
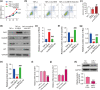
The dysfunction and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells are the initiating links in the formation of atherosclerosis. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an extremely extensive RNA methylation modification and its abnormality leads to the occurrence of various human diseases. In this study, we explored the effects of demethylase α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase ALKB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) on TNF-α-induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In TNF-α-treated HUVECs, the expression of ALKBH5 was significantly decreased. ALKBH5 overexpression promoted the proliferation and inhibited the apoptosis in TNF-α-treated HUVECs, suggesting that ALKBH5 had a protective effect on cell damage induced by TNF-α. Importantly, ALKBH5 promoted the expression of Bcl-2 in HUVECs. Bcl2 overexpression reduced the expression of Gadd45, Bax, and p21, which are transcriptionally activated by p53. But the expression of p53 has not been significantly affected, indicating that Bcl2 might regulate the apoptosis by inhibiting p53 downstream targets. In addition, ALKBH5 overexpression significantly increased the level of pri-miR-7 and decreased the level of miR-7. In conclusion, ALKBH5 attenuated the TNF-α-induced cell injury via promoting Bcl2 expression. Our research expands the understanding of the progression mechanism of atherosclerosis and provides a potential strategy for the protection of vascular endothelial injury.
Keywords: ALKBH5; Bcl-2; N6-methyladenosine; apoptosis; atherosclerosis.
© 2022 Xiaoshan Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 promotes tumor progression by inhibiting RIG-I expression and interferon alpha production through the IKKε/TBK1/IRF3 pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 9;21(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01572-2. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35395767 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH5 Alleviates Ultraviolet B Radiation-Induced Chronic Actinic Dermatitis via Regulating Pyroptosis.Inflammation. 2024 Feb;47(1):159-172. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01901-7. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 37740102
-
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner.Mol Cancer. 2020 May 19;19(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01158-w. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32429928 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH5 prevents hepatocellular carcinoma progression by post-transcriptional inhibition of PAQR4 in an m6A dependent manner.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jan 6;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00370-2. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36609413 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH5 Inhibited Cell Proliferation and Sensitized Bladder Cancer Cells to Cisplatin by m6A-CK2α-Mediated Glycolysis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Oct 22;23:27-41. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.031. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 33376625 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insights into RNA N6-methyladenosine and programmed cell death in atherosclerosis.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 3;30(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00901-z. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39227813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) writer METTL3 accelerates the apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells in high glucose.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 13;9(3):e13721. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13721. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36873555 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Nov 21;17(1):1788-1796. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0603. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 36457797 Free PMC article.
-
KLF7 reverses ox-LDL-induced ferroptosis in HMEC-1 cells through transcriptionally activating ALKBH5 to inhibit the m6A modification of ACSL4.Cytotechnology. 2024 Dec;76(6):653-666. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00641-2. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39435423
-
Expression patterns and clinical value of key m6A RNA modification regulators in smoking patients with coronary artery disease.Epigenetics. 2024 Dec;19(1):2392400. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2024.2392400. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39167728 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
