Epigenetic-structural changes in X chromosomes promote Xic pairing during early differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 35797402
- PMCID: PMC9174021
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v19.0018
Epigenetic-structural changes in X chromosomes promote Xic pairing during early differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
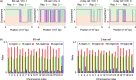
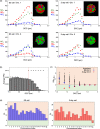
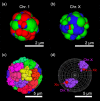
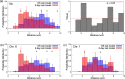
X chromosome inactivation center (Xic) pairing occurs during the differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells from female mouse embryos, and is related to X chromosome inactivation, the circadian clock, intra-nucleus architecture, and metabolism. However, the mechanisms underlying the identification and approach of X chromosome pairs in the crowded nucleus are unclear. To elucidate the driving force of Xic pairing, we developed a coarse-grained molecular dynamics model of intranuclear chromosomes in ES cells and in cells 2 days after the onset of differentiation (2-day cells) by considering intrachromosomal epigenetic-structural feature-dependent mechanics. The analysis of the experimental data showed that X-chromosomes exhibit the rearrangement of their distributions of open/closed chromatin regions on their surfaces during cell differentiation. By simulating models where the excluded volume effects of closed chromatin regions are stronger than those of open chromatin regions, such rearrangement of open/closed chromatin regions on X-chromosome surfaces promoted the mutual approach of the Xic pair. These findings suggested that local intrachromosomal epigenetic features may contribute to the regulation of cell species-dependent differences in intranuclear architecture.
Keywords: X chromosome; Xic pairing; embryonic stem cells.
2022 THE BIOPHYSICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PAR-TERRA directs homologous sex chromosome pairing.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Aug;24(8):620-631. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3432. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28692038 Free PMC article.
-
Sensing X chromosome pairs before X inactivation via a novel X-pairing region of the Xic.Science. 2007 Dec 7;318(5856):1632-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1149420. Science. 2007. PMID: 18063799
-
Role of the region 3' to Xist exon 6 in the counting process of X-chromosome inactivation.Nat Genet. 1998 Jul;19(3):249-53. doi: 10.1038/924. Nat Genet. 1998. PMID: 9662396
-
Cis- and trans-regulation in X inactivation.Chromosoma. 2016 Mar;125(1):41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0525-x. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26198462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X inactivation Xplained.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007 Oct;17(5):387-93. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007. PMID: 17869504 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Model of Nuclear Global Chromosomes Dynamics in Mammalian Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2856:281-292. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4136-1_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39283459
References
-
- Bacher, C. P., Guggiari, M., Brors, B., Augui, S., Clerc, P., Avner, P., et al. . Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 293–299 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1365 - PubMed
-
- Xu, N., Tsai, C.-L., Lee, J. T.. Transient homologous chromosome pairing marks the onset of X inactivation. Science 311, 1149–1152 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122984 - PubMed
-
- Masui, O., Bonnet, I., Le Baccon, P., Brito, I., Pollex, T., Murphy, N., et al. . Live-cell chromosome dynamics and outcome of X chromosome pairing events during ES cell differentiation. Cell 145, 447–458 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.032 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pollex, T., Heard, E.. Nuclear positioning and pairing of X-chromosome inactivation centers are not primary determinants during initiation of random X-inactivation. Nat. Genet. 51, 285–295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0305-7 - PubMed
-
- Payer, B., Lee, J. T.. X chromosome dosage compensation: How mammals keep the balance. Annu. Rev. Genet. 42, 733–772 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091711 - PubMed

