Role of Helical Structure in MBP Immunodominant Peptides for Efficient IgM Antibody Recognition in Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 35795217
- PMCID: PMC9250970
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.885180
Role of Helical Structure in MBP Immunodominant Peptides for Efficient IgM Antibody Recognition in Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
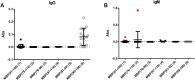
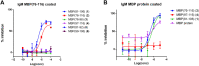
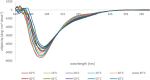
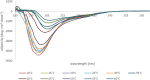
The involvement of Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) has been widely discussed in the literature. This intrinsically disordered protein has an interesting α-helix motif, which can be considered as a conformational epitope. In this work we investigate the importance of the helical structure in antibody recognition by MBP peptides of different lengths. Firstly, we synthesized the peptide MBP (81-106) (1) and observed that its elongation at both N- and C-termini, to obtain the peptide MBP (76-116) (2) improves IgM antibody recognition in SP-ELISA, but destabilizes the helical structure. Conversely, in competitive ELISA, MBP (81-106) (1) is recognized more efficiently by IgM antibodies than MBP (76-116) (2), possibly thanks to its more stable helical structure observed in CD and NMR conformational experiments. These results are discussed in terms of different performances of peptide antigens in the two ELISA formats tested.
Keywords: NMR; circular dichroism; immune response; multiple sclerosis; myelin basic protein antigen; peptide-antigen based ELISA; synthetic helical peptides.
Copyright © 2022 Staśkiewicz, Quagliata, Real-Fernandez, Nuti, Lanzillo, Brescia-Morra, Rusche, Jewginski, Carotenuto, Brancaccio, Aharoni, Arnon, Rovero, Latajka and Papini.
Conflict of interest statement
Author HR is employed by Fischer Analytics GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thermodynamic analysis of the disorder-to-α-helical transition of 18.5-kDa myelin basic protein reveals an equilibrium intermediate representing the most compact conformation.J Mol Biol. 2015 May 22;427(10):1977-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25816771
-
Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocyte repertoire in multiple sclerosis. Complexity of the response and dominance of nested epitopes due to recruitment of multiple T cell clones.J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2633-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI116879. J Clin Invest. 1993. PMID: 7504690 Free PMC article.
-
An IgM anti-MBP Ab in a case of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia with polyneuropathy expressing an idiotype reactive with an MBP epitope immunodominant in MS and EAE.J Neuroimmunol. 2001 Feb 1;113(1):163-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00425-2. J Neuroimmunol. 2001. PMID: 11137588
-
A review of T-cell receptors in multiple sclerosis: clonal expansion and persistence of human T-cells specific for an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 7;756:241-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb44522.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7544075 Review.
-
The classic basic protein of myelin--conserved structural motifs and the dynamic molecular barcode involved in membrane adhesion and protein-protein interactions.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Jun;10(3):196-215. doi: 10.2174/138920309788452218. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19519451 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed M. A. M., De Avila M., Polverini E., Bessonov K., Bamm V. V., Harauz G. (2012). Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Structure and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of a Murine 18.5 kDa Myelin Basic Protein Segment (S72-S107) in Association with Dodecylphosphocholine Micelles. Biochemistry 51, 7475–7487. 10.1021/bi300998x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

