Polo-like kinase 4 is associated with advanced TNM stages and reduced survival and its inhibition improves chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35782899
- PMCID: PMC9247664
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13389
Polo-like kinase 4 is associated with advanced TNM stages and reduced survival and its inhibition improves chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer
Abstract
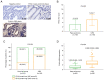
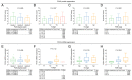
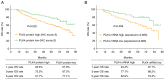
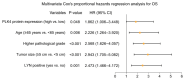
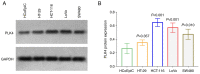
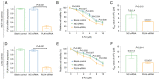
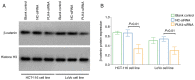
High expression of polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) promotes tumorigenesis and is correlated with poor prognosis in several kinds of cancer. However, the prognostic value of PLK4 in colorectal cancer (CRC) has not been elucidated. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between PLK4 and the prognosis and effect of PLK4 inhibition on chemosensitivity in CRC. A total of 142 patients with CRC were enrolled, and 142 pairs of CRC and para-carcinoma tissues were used to measure PLK4 protein expression using immunohistochemistry (IHC). Among them, 69 pairs were used to detect PLK4 mRNA expression using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. In addition, PLK4-small interfering RNA (siRNA) was transfected into CRC cells, followed by 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) treatment for it was a fundamental chemotherapy for CRC. In addition, western blotting was used to detect PLK4 protein expression among human colonic epithelial cell and human CRC cell lines, including HCT-116, LoVo, SW480 and HT-29, as well as nuclear translocation of β-catenin. The IHC score and mRNA expression of PLK4 were higher in CRC tissues compared with para-carcinoma tissues (both P<0.001). Furthermore, the IHC score of tumor PLK4 was not correlated with pathological grade (P=0.585), T stage (P=0.357), N stage (P=0.107225) or tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (P=0.093). The mRNA expression of tumor PLK4 was positively correlated with N stage (P=0.019) and TNM stage (P=0.004), but not with pathological grade (P=0.498) or T stage (P=0.112). Of note, the high protein expression of tumor PLK4 was an independent factor for poor overall survival (OS; P=0.048). In addition, PLK4 was elevated in CRC cell lines; PLK4-siRNA reduced the 50% inhibitory concentration value of 5-FU in HCT-116 (4.4±0.1 µM vs. 7.6±1.4 µM) and LoVo cells (5.5±0.6 µM vs. 9.9±1.8 µM) (both P<0.05). Besides, PLK4-siRNA decreased nuclear translocation of β-catenin. In conclusion, the high expression of tumor PLK4 was associated with advanced TNM stage and shorter OS in patients with CRC. In addition, targeting PLK4 improved chemosensitivity in CRC cells.
Keywords: chemosensitivity; colorectal cancer; overall survival; polo-like kinase 4; tumor-node-metastasis stage.
Copyright: © Duan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase D1 Correlates with Less Lymph Node Metastasis Risk, Enhanced 5-FU Sensitivity, and Better Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2023 Aug 11;260(4):305-314. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2023.J042. Epub 2023 May 25. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37225445
-
Polo-Like Kinase 4 Correlates with Aggressive Tumor Characteristics, Shortened Disease-Free Survival and Overall Survival in Patients with Cutaneous Melanoma who Undergo Surgical Resection.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2024 Apr 26;262(4):253-261. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2023.J092. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 37940564
-
Aberrant expression of polo-like kinase 4 in renal cell carcinoma: Association with clinicopathological characteristics and long-term survival.Oncol Lett. 2022 Oct 14;24(6):427. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13547. eCollection 2022 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36311683 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 4 correlates with greater tumor size, lymph node metastasis and confers poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Apr;34(4):e23152. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23152. Epub 2019 Dec 25. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31876063 Free PMC article.
-
PLK4 is a key molecule in the formation of PGCCs and promotes invasion and migration of progeny cells derived from PGCCs.J Cancer. 2022 Jul 18;13(9):2954-2969. doi: 10.7150/jca.74211. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35912011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tumor polo-like kinase 4 protein expression reflects lymphovascular invasion, higher Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage, and shortened survival in endometrial cancer patients who undergo surgical resection.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-02911-9. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38326803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkins T, McMechan D, Talukder A. Colorectal cancer screening and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2018;97:658–665. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
