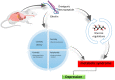
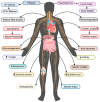
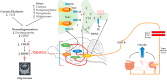
Ghrelin mediated regulation of neurosynaptic transmitters in depressive disorders
- PMID: 35782191
- PMCID: PMC9240712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100113
Ghrelin mediated regulation of neurosynaptic transmitters in depressive disorders
Abstract
Ghrelin is a peptide released by the endocrine cells of the stomach and the neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. It modulates both peripheral and central functions. Although ghrelin has emerged as a potent stimulator of growth hormone release and as an orexigenic neuropeptide, the wealth of literature suggests its involvement in the pathophysiology of affective disorders including depression. Ghrelin exhibits a dual role through the advancement and reduction of depressive behavior with nervousness in the experimental animals. It modulates depression-related signals by forming neuronal networks with various neuropeptides and classical neurotransmitter systems. The present review emphasizes the integration and signaling of ghrelin with other neuromodulatory systems concerning depressive disorders. The role of ghrelin in the regulation of neurosynaptic transmission and depressive illnesses implies that the ghrelin system modulation can yield promising antidepressive therapies.
Keywords: Depression; GHSR; Ghrelin; Neurotransmitter; Psychotic disorders.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ghrelin/GHSR System in Depressive Disorder: Pathologic Roles and Therapeutic Implications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 10;46(7):7324-7338. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070434. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal circuits involving ghrelin in the hypothalamus-mediated regulation of feeding.Neuropeptides. 2010 Apr;44(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.11.010. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20036003 Review.
-
Ghrelin: a novel peptide for growth hormone release and feeding regulation.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002 Jul;5(4):391-5. doi: 10.1097/00075197-200207000-00007. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002. PMID: 12107374 Review.
-
Ghrelin receptors mediate ghrelin-induced excitation of agouti-related protein/neuropeptide Y but not pro-opiomelanocortin neurons.J Neurochem. 2017 Aug;142(4):512-520. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14080. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28547758
-
Ghrelin in central neurons.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009 Mar;7(1):37-49. doi: 10.2174/157015909787602779. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19721816 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin system in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023 Feb;78:102655. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102655. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36527939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective 5-HT6 Receptor Ligands (Agonist and Antagonist) Show Different Effects on Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Metabolic Dysfunctions in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;16(2):154. doi: 10.3390/ph16020154. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259305 Free PMC article.
-
Oleocanthal Ameliorates Metabolic and Behavioral Phenotypes in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Jul 23;28(14):5592. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145592. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513464 Free PMC article.
-
New antidepressant mechanism of Yueju Pill: Increasing ghrelin level by inhibiting gastric mTOR/S6K signaling pathway and sensitizing hippocampal GHS-R.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(17):e37038. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37038. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abizaid A., Liu Z.-W., Andrews Z.B., Shanabrough M., Borok E., Elsworth J.D., Roth R.H., Sleeman M.W., Picciotto M.R., Tschöp M.H., Gao X.-B., Horvath T.L. Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite. J. Clin. Invest. 2006;116:3229–3239. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Açıkel B., Hoşoğlu E., Artik A., Yerlikaya F. Increased serum nesfatin-1 levels among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder. Arch. Clin. Psychiatry (São Paulo) 2021;48:16–19.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources