Therapeutic potential of targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) by small molecule inhibitors
- PMID: 35781678
- PMCID: PMC9474610
- DOI: 10.1002/ddr.21971
Therapeutic potential of targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) by small molecule inhibitors
Abstract
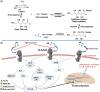
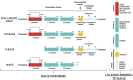
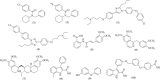
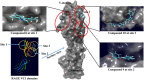
Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a 45 kDa transmembrane receptor of immunoglobulin family that can bind to various endogenous and exogenous ligands and initiate the inflammatory downstream signaling pathways. RAGE is involved in various disorders including cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and diabetes. This review summarizes the structural features of RAGE and its various isoforms along with their pathological effects. Mainly, the article emphasized on the translational significance of antagonizing the interactions of RAGE with its ligands using small molecules reported in the last 5 years and discusses future approaches that could be employed to block the interactions in the treatment of chronic inflammatory ailments. The RAGE inhibitors described in this article could prove as a powerful approach in the management of immune-inflammatory diseases. A critical review of the literature suggests that there is a dire need to dive deeper into the molecular mechanism of action to resolve critical issues that must be addressed to understand RAGE-targeting therapy and long-term blockade of RAGE in human diseases.
Keywords: AGEs; RAGE; RAGE isoforms; S100 proteins; antagonist; chronic inflammatory diseases; endogenous ligands; exogenous ligands; inhibitor.
© 2022 The Authors. Drug Development Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAGE and its ligands: from pathogenesis to therapeutics.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Dec;55(6):555-575. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1819194. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32933340
-
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs), Glutathione and Breast Cancer: Factors, Mechanism and Therapeutic Interventions.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(1):65-71. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180912104342. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 30207227
-
Targeting the Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE): A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective.J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 14;60(17):7213-7232. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00058. Epub 2017 May 19. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28482155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characteristics of RAGE and Advances in Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 27;22(13):6904. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136904. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products: a mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 1999 Mar 19;84(5):489-97. doi: 10.1161/01.res.84.5.489. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10082470 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Treatment of ARDS.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;13(21):3296. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213296. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the HMGB1/RAGE Axis in Inflammatory Diseases.Molecules. 2022 Oct 27;27(21):7311. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217311. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAGE Inhibitors in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 9;11(4):1131. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041131. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1/RAGE axis in tumor development: unraveling its significance.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 1;14:1336191. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1336191. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38529373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 12;8(1):267. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01486-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37433768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad, S. S. , Khan, H. , Danish Rizvi, S. M. , Ansari, S. A. , Ullah, R. , Rastrelli, L. , & Siddiqui, M. H. (2019). Computational study of natural compounds for the clearance of amyloid‐betaeta: A potential therapeutic management strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Molecules , 24(18). 10.3390/molecules24183233 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

