Plasma Homocysteine Level Is Independently Associated With Conventional Atherogenic Lipid Profile and Remnant Cholesterol in Adults
- PMID: 35770226
- PMCID: PMC9234129
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.898305
Plasma Homocysteine Level Is Independently Associated With Conventional Atherogenic Lipid Profile and Remnant Cholesterol in Adults
Abstract
Background: Homocysteine (Hcy) is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, while mechanisms are unclear. Despite inconsistent and limited, epidemiological and experimental studies indicated that hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) affected lipid metabolism. This study aims to investigate the association of plasma Hcy with traditional lipid profiles and remnant cholesterol (RC) in Chinese adults.
Methods: In total, 7,898 subjects aged 20-79 years who underwent a physical examination at Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital in Beijing were included in this study. Fasting plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)], Hcy, and other metabolic risk factors were measured by routine automated laboratory methods. RC was calculated as TC minus HDL-C and LDL-C. The linear regression model and logistic regression model were used to assess the relationship between Hcy and lipids after adjusting potential confounders.
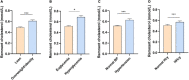
Results: Of the subjects, the median level of plasma Hcy was 13.0 μmol/L and 32.3% had HHcy. Plasma Hcy was negatively associated with HDL-C, ApoA1, and Lp(a) and positively associated with TG levels after adjusting age, sex, body mass index, blood pressure, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, creatinine, uric acid, and glucose. HHcy significantly increased the risk of low HDL-C [odds ratio (OR) 1.26; 95%CI (1.11-1.44); p < 0.001]. The net mediation effects of ApoA1 on the relationship between Hcy and HDL-C before and after adjusting confounders were 46.9 and 30.6%, respectively. More interestingly, the RC level was significantly elevated in subjects with HHcy after adjusting other influencing factors (p = 0.025). Hcy presented a positive correlation with RC levels after adjusting the above confounding factors (β = 0.073, p = 0.004), and the correlation was still significant even after controlling other lipids, including TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, ApoA1, ApoB, and Lp(a).
Conclusion: Our study showed that plasma Hcy was not only significantly associated with conventional atherogenic lipids but also independently correlated with RC levels beyond other lipids after controlling potential confounders. This finding proposes that identifying Hcy-related dyslipidemia risk, both traditional lipids and RC residual risk, is clinically relevant as we usher in a new era of targeting Hcy-lowering therapies to fight against dyslipidemia or even cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Chinese adults; apolipoprotein A1; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; homocysteine; remnant cholesterol; triglyceride.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Liu, An, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between plasma homocysteine level and lipid profiles in a community-based Chinese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Mar 14;16(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0441-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28288621 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of hyperhomocysteinemia on the lipid profiles and lipid ratios between patients with and without coronary artery disease: A retrospective observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 30;101(52):e32464. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032464. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36595992 Free PMC article.
-
A Cross-sectional Study on the Relationship Between Homocysteine and Lipid Profiles Among Chinese Population from Hunan.Lipids. 2021 Jan;56(1):93-100. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12279. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Lipids. 2021. PMID: 32954499
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
-
Targeting low HDL-cholesterol to decrease residual cardiovascular risk in the managed care setting.J Manag Care Pharm. 2008 Oct;14(8 Suppl):S3-28; quiz S30-1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008. PMID: 19891279 Review.
Cited by
-
Homocysteine concentration in coronary artery disease and severity of coronary lesions.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18474. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18474. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896027 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of homocysteine-mediated endothelial injury and its consequences for atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 16;9:1109445. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1109445. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36727029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia and its effect on ageing and language functions - HEAL study.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 29;14(1):20101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69818-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39209902 Free PMC article.
-
Linking homocysteine and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease: insights and implications.Apoptosis. 2024 Dec;29(11-12):1944-1958. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01999-6. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 39044092 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

