Diastolic Filling Time, Chronotropic Response, and Exercise Capacity in Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction With Sinus Rhythm
- PMID: 35766289
- PMCID: PMC9333393
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.026009
Diastolic Filling Time, Chronotropic Response, and Exercise Capacity in Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction With Sinus Rhythm
Abstract
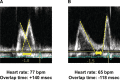
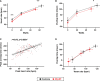
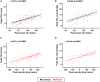
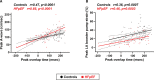
Background Exercise-induced high heart rate may impair exercise tolerance by reducing diastolic filling time and ventricular filling in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Given the importance of chronotropic response, we hypothesized that reduction in diastolic filling time because of exercise-induced increased heart rate would not impair cardiac output reserve and exercise capacity. We sought to determine the association between heart rate, diastolic filling time, hemodynamics, and exercise capacity in HFpEF. Methods and Results Patients with HFpEF (n=66) and controls without HF (n=107) underwent bicycle exercise echocardiography with simultaneous expired gas analysis to measure oxygen consumption. Diastolic filling time was assessed by the overlap time between mitral E- and A-waves (longer overlap time indicates shorter diastolic filling duration). Overlap time increased (ie, diastolic filling time shortened) in HFpEF and controls as heart rate increased with exercise, and the relationship was similar between the groups. Greater heart rate response correlated with higher cardiac output (r=0.51, P<0.0001) and oxygen consumption (r=0.50, P<0.0001) during peak exercise. Shorter diastolic filling time, as assessed by longer overlap time, was correlated with higher cardiac output (r=0.47, P<0.0001) and peak oxygen consumption (r=0.38, P=0.007), not with E/e' or right ventricular-pulmonary artery uncoupling. Longer overlap time was associated with mitral A velocity (r=0.53, P<0.0001) and left atrial booster pump strain (r=0.42, P<0.0001). Conclusions Shortening of diastolic filling interval in tandem with increased heart rate during exercise does not limit cardiac output reserve or exercise capacity in HFpEF.
Keywords: chronotropic incompetence; diastolic filling time; exercise; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of If-channel inhibition on hemodynamic status and exercise tolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a randomized trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 8;62(15):1330-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.043. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23916925 Clinical Trial.
-
Contributions of Nondiastolic Factors to Exercise Intolerance in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Feb 16;67(6):659-670. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.10.096. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26868691
-
Functional iron deficiency and diastolic function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 12;168(5):4652-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.185. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23968714
-
Relative Impairments in Hemodynamic Exercise Reserve Parameters in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Study-Level Pooled Analysis.JACC Heart Fail. 2018 Feb;6(2):117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.10.014. JACC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29413366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on left ventricular diastolic function, exercise capacity, and quality of life in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Heart Vessels. 2019 Apr;34(4):597-606. doi: 10.1007/s00380-018-1279-1. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Heart Vessels. 2019. PMID: 30315496 Review.
Cited by
-
Contributions of anemia to exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction-An exercise stress echocardiographic study.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2023 Aug 20;48:101255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2023.101255. eCollection 2023 Oct. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2023. PMID: 37794956 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ivabradine on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function of Patients With Preserved Ejection Fraction - Results of the IVA-PEF Study.Circ Rep. 2022 Sep 22;4(10):499-504. doi: 10.1253/circrep.CR-22-0067. eCollection 2022 Oct 7. Circ Rep. 2022. PMID: 36304432 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond weight loss: the potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Heart Fail Rev. 2025 Jan;30(1):17-38. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10438-2. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 39269643 Review.
-
Study on the relationship between body mass index and blood pressure indices in children aged 7-17 during COVID-19.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 19;12:1409214. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1409214. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38962763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

