Juvenile hormone promotes paracellular transport of yolk proteins via remodeling zonula adherens at tricellular junctions in the follicular epithelium
- PMID: 35759519
- PMCID: PMC9269875
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010292
Juvenile hormone promotes paracellular transport of yolk proteins via remodeling zonula adherens at tricellular junctions in the follicular epithelium
Abstract
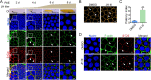
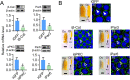
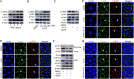
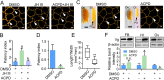
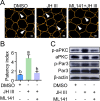
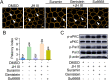
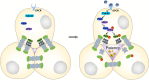
Juvenile hormone (JH) acts as a gonadotrophic hormone stimulating insect vitellogenesis and oogenesis. Paracellular transport of yolk proteins through intercellular channels (patency) in the follicular epithelium is a developmentally regulated and evolutionarily conserved process during vitellogenesis. However, the mechanisms underlying patency opening are poorly understood. Using the migratory locust Locusta migratoria as a model system, we report here that JH-regulated remodeling of zonula adherens (ZA), the belt-like adherens junction maintaining physical linking between follicle cells controlled the opening of patency. JH triggered phosphorylation of Partitioning defective protein 3 (Par3) via a signaling cascade including G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), small GTPase Cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) and atypical Protein kinase C (aPKC). Par3 phosphorylation resulted in its disassociation from β-Catenin, the cytoplasmic partner of ZA core component E-Cadherin. Release of Par3 from the β-Catenin/E-Cadherin complex caused ZA disassembly at tricellular contacts, consequently leading to patency enlargement. This study provides new insight into how JH stimulates insect vitellogenesis and egg production via inducing the opening of paracellular route for vitellogenin transport crossing the follicular epithelium barrier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C mediates juvenile hormone-dependent phosphorylation of Na+/K+-ATPase to induce ovarian follicular patency for yolk protein uptake.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 28;293(52):20112-20122. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005692. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30385509 Free PMC article.
-
Transient opening of tricellular vertices controls paracellular transport through the follicle epithelium during Drosophila oogenesis.Dev Cell. 2021 Apr 19;56(8):1083-1099.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.03.021. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 33831351
-
Argonaute 1 is indispensable for juvenile hormone mediated oogenesis in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;43(9):879-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23792802
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 28;8:593613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.593613. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A central role for cadherin signaling in cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Sep 1;358(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28412244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microsporidian Nosema bombycis hijacks host vitellogenin and restructures ovariole cells for transovarial transmission.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Dec 7;19(12):e1011859. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011859. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38060601 Free PMC article.
-
Cyp6g2 is the major P450 epoxidase responsible for juvenile hormone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster.BMC Biol. 2024 May 13;22(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01910-4. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38741075 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Characteristics and Energy Metabolism of Migrating Insects.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 17;13(3):439. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030439. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Juvenile hormone signaling is indispensable for late embryogenesis in ametabolous and hemimetabolous insects.BMC Biol. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02029-2. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39394161 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-989 targets 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor1 to regulate ovarian development and eggs production in Culex pipiens pallens.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Sep 13;16(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05957-0. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37705064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wyatt GR, Davey KG. Cellular and molecular actions of juvenile hormone. II. Roles of juvenile hormone in adult insects. In: Evans PD, editor. Advances in insect physiology. London: Academic Press Ltd-Elsevier Science Ltd; 1996. p. 1–155.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

