The Emerging Role of Plant-Derived Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles in Immune Regulation and Periodontitis Treatment
- PMID: 35757759
- PMCID: PMC9231591
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.896745
The Emerging Role of Plant-Derived Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles in Immune Regulation and Periodontitis Treatment
Abstract
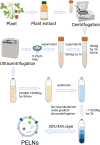
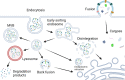
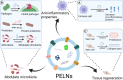
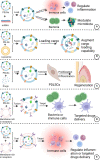
Periodontitis is an infectious oral disease, which leads to the destruction of periodontal tissues and tooth loss. Although the treatment of periodontitis has improved recently, the effective treatment of periodontitis and the periodontitis-affected periodontal tissues is still a challenge. Therefore, it is urgent to explore new therapeutic strategies for periodontitis. Natural products show anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and bone protective effects to periodontitis and most of these natural products are safe and cost-effective. Among these, the plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PELNs), a type of natural nanocarriers repleted with lipids, proteins, RNAs, and other active molecules, show the ability to enter mammalian cells and regulate cellular activities. Reports from the literature indicate the great potential of PELNs in the regulation of immune functions, inflammation, microbiome, and tissue regeneration. Moreover, PELNs can also be used as drug carriers to enhance drug stability and cellular uptake in vivo. Since regulation of immune function, inflammation, microbiome, and tissue regeneration are the key phenomena usually targeted during periodontitis treatment, the PELNs hold the promising potential for periodontitis treatment. This review summarizes the recent advances in PELNs-related research that are related to the treatment of periodontitis and regeneration of periodontitis-destructed tissues and the underlying mechanisms. We also discuss the existing challenges and prospects of the application of PELNs-based therapeutic approaches for periodontitis treatment.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; oral tissue regeneration; periodontitis; plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Yu, Zhu, Zeng, Xu, Cheng, Ouyang, Chen, Pathak, Wu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current understanding of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles in regulating the inflammatory response and immune system microenvironment.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Apr;190:106733. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106733. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36931541 Review.
-
[Research progress on plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their applications].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Nov;48(22):5977-5984. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230721.602. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114203 Chinese.
-
Research status and challenges of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 May;174:116543. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116543. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38608523 Review.
-
Exosome-like nanoparticles derived from fruits, vegetables, and herbs: innovative strategies of therapeutic and drug delivery.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 1;14(12):4598-4621. doi: 10.7150/thno.97096. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39239509 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Sep 5;18:4987-5009. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S420748. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37693885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From bench to bedside: The promising value of exosomes in precision medicine for CNS tumors.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 6;10(11):e32376. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32376. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38961907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dual Effects of Exosomes on Glioma: A Comprehensive Review.J Cancer. 2023 Sep 4;14(14):2707-2719. doi: 10.7150/jca.86996. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37779868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Immune Responses against Antigen-Specific Presentation.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;10(10):1691. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101691. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of miRNA profiling in konjac-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and elucidation of their multifaceted roles in human health.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 8;15:1444683. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1444683. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39175488 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in delivery systems for CRISPR/Cas-mediated cancer treatment: a focus on viral vectors and extracellular vesicles.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1444437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

