Possible Neuropathology of Sleep Disturbance Linking to Alzheimer's Disease: Astrocytic and Microglial Roles
- PMID: 35755779
- PMCID: PMC9218054
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.875138
Possible Neuropathology of Sleep Disturbance Linking to Alzheimer's Disease: Astrocytic and Microglial Roles
Abstract
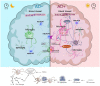
Sleep disturbances not only deteriorate Alzheimer's disease (AD) progress by affecting cognitive states but also accelerate the neuropathological changes of AD. Astrocytes and microglia are the principal players in the regulation of both sleep and AD. We proposed that possible astrocyte-mediated and microglia-mediated neuropathological changes of sleep disturbances linked to AD, such as astrocytic adenosinergic A1, A2, and A3 regulation; astrocytic dopamine and serotonin; astrocyte-mediated proinflammatory status (TNFα); sleep disturbance-attenuated microglial CX3CR1 and P2Y12; microglial Iba-1 and astrocytic glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP); and microglia-mediated proinflammatory status (IL-1b, IL-6, IL-10, and TNFα). Furthermore, astrocytic and microglial amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau in AD were reviewed, such as astrocytic Aβ interaction in AD; astrocyte-mediated proinflammation in AD; astrocytic interaction with Aβ in the central nervous system (CNS); astrocytic apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-induced Aβ clearance in AD, as well as microglial Aβ clearance and aggregation in AD; proinflammation-induced microglial Aβ aggregation in AD; microglial-accumulated tau in AD; and microglial ApoE and TREM2 in AD. We reviewed astrocytic and microglial roles in AD and sleep, such as astrocyte/microglial-mediated proinflammation in AD and sleep; astrocytic ApoE in sleep and AD; and accumulated Aβ-triggered synaptic abnormalities in sleep disturbance. This review will provide a possible astrocytic and microglial mechanism of sleep disturbance linked to AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid beta; astrocyte; microglia; sleep disturbance.
Copyright © 2022 Xiao, Liu, Lu, Sha, Xu, Yu and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective reduction of astrocyte apoE3 and apoE4 strongly reduces Aβ accumulation and plaque-related pathology in a mouse model of amyloidosis.Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Feb 2;17(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00516-0. Mol Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35109920 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease: Roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress.Neurobiol Stress. 2018 May 19;9:9-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2018.05.003. eCollection 2018 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2018. PMID: 29992181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoproteins E and J interfere with amyloid-beta uptake by primary human astrocytes and microglia in vitro.Glia. 2014 Apr;62(4):493-503. doi: 10.1002/glia.22619. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24446231
-
Müller cell degeneration and microglial dysfunction in the Alzheimer's retina.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Oct 5;10(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01448-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36199154 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hierarchy of Coupled Sleep Oscillations Reverses with Aging in Humans.J Neurosci. 2023 Sep 6;43(36):6268-6279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0586-23.2023. Epub 2023 Aug 16. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37586871 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Chronic Sleep Deprivation to Age-Related Neurodegeneration in a Mouse Model of Familial Alzheimer's Disease (5xFAD).Neurol Int. 2023 Jun 27;15(3):778-791. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15030049. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37489355 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep deprivation: A risk factor for the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 5;10(7):e28819. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28819. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38623196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep deprivation in adolescent mice impairs long-term memory till early adulthood via suppression of hippocampal astrocytes.Sleep. 2024 Oct 11;47(10):zsae143. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsae143. Sleep. 2024. PMID: 38934552 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: P2X7 receptor modulation is a viable therapeutic target for neurogenic pain with concurrent sleep disorders.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 30;17:1293174. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1293174. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38099200 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Apelt J., Ach K., Schliebs R. (2003). Aging-related down-regulation of neprilysin, a putative β-amyloid-degrading enzyme, in transgenic Tg2576 Alzheimer-like mouse brain is accompanied by an astroglial upregulation in the vicinity of β-amyloid plaques. Neurosci. Lett. 339 183–186. 10.1016/S0304-3940(03)00030-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

