Digital breast tomosynthesis-based peritumoral radiomics approaches in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions
- PMID: 35748203
- PMCID: PMC9634934
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2022.20664
Digital breast tomosynthesis-based peritumoral radiomics approaches in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions
Abstract
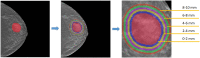
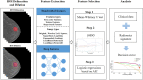
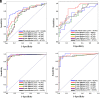
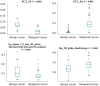
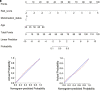
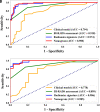
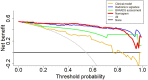
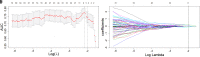
PURPOSE We aimed to evaluate digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT)-based radiomics in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions in women. METHODS A total of 185 patients who underwent DBT scans were enrolled between December 2017 and June 2019. The features of handcrafted and deep learning-based radiomics were extracted from the tumoral and peritumoral regions with different radial dilation distances outside the tumor. A 3-step method was used to select discriminative features and develop the radiomics signature. Discriminative clinical factors were identified by univariate logistic regression. The clinical fac- tors with P < .05 were used to build a clinical model with multivariate logistic regression. The radiomics nomogram was developed by integrating the radiomics signature and discriminative clinical factors. Discriminative performance of the radiomics signature, clinical model, nomo- gram, and breast imaging reporting and data system assessment were evaluated and compared with the receiver operating characteristic and decision curves analysis (DCA). RESULTS A total of 2 handcrafted and 2 deep features were identified as the most discriminative features from the peritumoral regions with 2 mm dilation distances and used to develop the radiomics signature. The nomogram incorporating the radiomics signature, age, and menstruation status showed the best discriminative performance with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.980 (95% CI, 0.960 to 1.000; sensitivity =0.970, specificity =0.946) in the training cohort and 0.985 (95% CI, 0.960 to 1.000; sensitivity = 0.909, specificity = 0.966) in the validation cohort. DCA con- firmed the potential clinical usefulness of our nomogram. CONCLUSION Our results illustrate that the radiomics nomogram integrating the DBT imaging features and clinical factors (age and menstruation status) can be considered as a useful tool in aiding the clinical diagnosis of breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of an Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics Nomogram Using Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Preoperative Assessment of Lymphovascular Invasion in Invasive Breast Cancer.Acad Radiol. 2024 May;31(5):1748-1761. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.11.010. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38097466
-
Intratumoral and Peritumoral Analysis of Mammography, Tomosynthesis, and Multiparametric MRI for Predicting Ki-67 Level in Breast Cancer: a Radiomics-Based Study.Mol Imaging Biol. 2022 Aug;24(4):550-559. doi: 10.1007/s11307-021-01695-w. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022. PMID: 34904187
-
Multi-parametric MRI-based peritumoral radiomics on prediction of lymph-vascular space invasion in early-stage cervical cancer.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2022 Jul;28(4):312-321. doi: 10.5152/dir.2022.20657. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35731710 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Analysis on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Preoperative Evaluation of Lymphovascular Invasion Status in Invasive Breast Cancer.Acad Radiol. 2022 Dec;29(12):1773-1782. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.03.011. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35400556
-
Radiomic Evaluations of the Diagnostic Performance of DM, DBT, DCE MRI, DWI, and Their Combination for the Diagnosisof Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 10;11:725922. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.725922. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34568055 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
AI-based strategies in breast mass ≤ 2 cm classification with mammography and tomosynthesis.Breast. 2024 Dec;78:103805. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103805. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Breast. 2024. PMID: 39321503 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Ki-67 expression levels in breast cancer using radiomics-based approaches on digital breast tomosynthesis and ultrasound.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 11;14:1403522. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1403522. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39055558 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical-radiomic models based on digital breast tomosynthesis images: a preliminary investigation of a predictive tool for cancer diagnosis.Front Oncol. 2023 May 12;13:1152158. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1152158. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37251915 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced mammography and breast MRI in the diagnosis of breast cancer and detection of tumor size.Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Dec 11;54(1):249-261. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5786. eCollection 2024. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38812642 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a weakly supervised deep learning framework for breast cancer diagnosis with HR status based on mammography images.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Aug 18;22:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.08.012. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37655162 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

