Metabolomics Analysis of PK-15 Cells with Pseudorabies Virus Infection Based on UHPLC-QE-MS
- PMID: 35746630
- PMCID: PMC9229976
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061158
Metabolomics Analysis of PK-15 Cells with Pseudorabies Virus Infection Based on UHPLC-QE-MS
Abstract
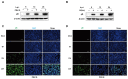
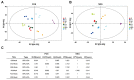
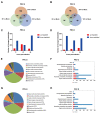
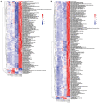
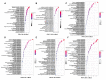
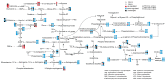
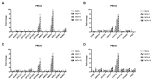
Viruses depend on the metabolic mechanisms of the host to support viral replication. We utilize an approach based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/Q Exactive HF-X Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass (UHPLC-QE-MS) to analyze the metabolic changes in PK-15 cells induced by the infections of the pseudorabies virus (PRV) variant strain and Bartha K61 strain. Infections with PRV markedly changed lots of metabolites, when compared to the uninfected cell group. Additionally, most of the differentially expressed metabolites belonged to glycerophospholipid metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, purine metabolism, and pyrimidine metabolism. Lipid metabolites account for the highest proportion (around 35%). The results suggest that those alterations may be in favor of virion formation and genome amplification to promote PRV replication. Different PRV strains showed similar results. An understanding of PRV-induced metabolic reprogramming will provide valuable information for further studies on PRV pathogenesis and the development of antiviral therapy strategies.
Keywords: PK-15 cells; UHPLC-QE-MS; metabolomic analysis; pseudorabies virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Untargeted LC-MS based metabolomic profiling of iPAMs to investigate lipid metabolic pathways alternations induced by different Pseudorabies virus strains.Vet Microbiol. 2021 May;256:109041. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109041. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Vet Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33813308
-
Metabolomics Exploration of Pseudorabies Virus Reprogramming Metabolic Profiles of PK-15 Cells to Enhance Viral Replication.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jan 29;10:599087. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.599087. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33585273 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of a novel pathogenic recombinant virus from Bartha vaccine and variant pseudorabies virus in China.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 May;68(3):1454-1464. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13813. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 32857916
-
Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Sep;69(3):462-500. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.3.462-500.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16148307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Pseudorabies Virus Variants: Genomics, Vaccination, Transmission, and Zoonotic Potential.Viruses. 2022 May 9;14(5):1003. doi: 10.3390/v14051003. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic regions associated with pseudorabies virus infection status in naturally infected feral swine (Sus scrofa).Front Genet. 2023 Nov 23;14:1292671. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1292671. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38075681 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

