Improving Dietary Intake of Essential Nutrients Can Ameliorate Inflammation in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- PMID: 35745123
- PMCID: PMC9228459
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14122393
Improving Dietary Intake of Essential Nutrients Can Ameliorate Inflammation in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Abstract
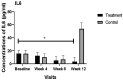
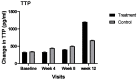
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are classified as chronic wounds and are one of the most common complications of diabetes. In chronic wounds, management of inflammation is a key step in treatment. Nutrition plays an important role in managing and controlling inflammation. This study evaluated the effects of nutrition supplementation and education on inflammatory biomarkers in patients with DFUs. Eligible patients with foot ulcers were randomly assigned to either a treatment (n = 15) or control group (n = 14). Both groups received standard care for wound treatment from the clinic; however, the treatment group was also provided with nutritional supplementation and education. Plasma concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers, namely C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL6), interleukin 10 (IL10), and tristetraprolin (TTP), were evaluated at baseline and every four weeks, until complete wound closure had occurred or up to 12 weeks. The mean plasma concentration of IL6 significantly decreased in the treatment group (p = 0.001). The interaction between time and group was not statistically significant for the mean plasma concentrations of CRP, IL10, and TTP during the 12 weeks of the study. The results of this study showed the positive effects of nutritional intervention on controlling inflammation in DFU patients. More clinical trials with a larger population and longer duration of time are needed to confirm our results.
Keywords: CRP; IL10; IL6; TTP; anti-inflammatory cytokines; chronic wounds; cytokines; diabetes; diabetic foot ulcer; inflammation; nutrient supplementation; nutrition education; nutrition intervention; pro-inflammatory cytokines; tristetraprolin; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poorly designed research does not help clarify the role of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.Diving Hyperb Med. 2016 Sep;46(3):133-134. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016. PMID: 27723012
-
A pilot study evaluating non-contact low-frequency ultrasound and underlying molecular mechanism on diabetic foot ulcers.Int Wound J. 2014 Dec;11(6):586-93. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12005. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Int Wound J. 2014. PMID: 23163982 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nutritional Supplementation Concurrent with Nutrition Education Accelerates the Wound Healing Process in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 3;8(8):263. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8080263. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32756299 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CXCL8 in chronic nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers and phenotypic changes in fibroblasts: a molecular perspective.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1565-1572. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07144-3. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35044539 Review.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.Health Technol Assess. 2000;4(21):1-237. Health Technol Assess. 2000. PMID: 11074391 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Nutrition Intervention on Blood Glucose, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Obese and Overweight Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 30;14(17):3564. doi: 10.3390/nu14173564. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36079822 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exploring the Interrelationships between Diabetes, Nutrition, Anxiety, and Depression: Implications for Treatment and Prevention Strategies.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 30;15(19):4226. doi: 10.3390/nu15194226. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical therapy in diabetic foot ulcer: Research progress and clinical application.Int Wound J. 2023 Oct;20(8):3417-3434. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14196. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 37095726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Nutrients for Optimal Blood Glucose Control and Mental Health in Individuals with Diabetes: A Review of the Evidence.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 10;15(18):3929. doi: 10.3390/nu15183929. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Patients with Venous Ulcers: A Clinical Trial.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 26;11(19):5683. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195683. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Association for the Advancement of Wound Care (AAWC) How to Heal a Wound and Find a Wound Clinic. 2016. [(accessed on 29 November 2016)]. Available online: http://aawconline.org/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

