Automated Open-Hardware Multiwell Imaging Station for Microorganisms Observation
- PMID: 35744447
- PMCID: PMC9227061
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13060833
Automated Open-Hardware Multiwell Imaging Station for Microorganisms Observation
Abstract
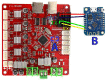
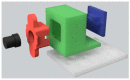
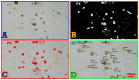
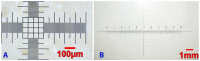
Bright field microscopes are particularly useful tools for biologists for cell and tissue observation, phenotyping, cell counting, and so on. Direct cell observation provides a wealth of information on cells' nature and physiological condition. Microscopic analyses are, however, time-consuming and usually not easy to parallelize. We describe the fabrication of a stand-alone microscope able to automatically collect samples with 3D printed pumps, and capture images at up to 50× optical magnification with a digital camera at a good throughput (up to 24 different samples can be collected and scanned in less than 10 min). Furthermore, the proposed device can store and analyze pictures using computer vision algorithms running on a low power integrated single board computer. Our device can perform a large set of tasks, with minimal human intervention, that no single commercially available machine can perform. The proposed open-hardware device has a modular design and can be freely reproduced at a very competitive price with the use of widely documented and user-friendly components such as Arduino, Raspberry pi, and 3D printers.
Keywords: IoT; bio-automation; edge computing; microbiology; microscopy; open-hardware.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design of a 3D printed smartphone microscopic system with enhanced imaging ability for biomedical applications.J Microsc. 2019 Oct;276(1):13-20. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12829. Epub 2019 Sep 22. J Microsc. 2019. PMID: 31498428
-
PiRamid: A compact Raspberry Pi imaging box to automate small-scale time-lapse digital analysis, suitable for laboratory and field use.HardwareX. 2022 Nov 15;12:e00377. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2022.e00377. eCollection 2022 Oct. HardwareX. 2022. PMID: 36437840 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting open source 3D printer architecture for laboratory robotics to automate high-throughput time-lapse imaging for analytical microbiology.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 19;14(11):e0224878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224878. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31743346 Free PMC article.
-
Open Hardware for Microfluidics: Exploiting Raspberry Pi Singleboard Computer and Camera Systems for Customisable Laboratory Instrumentation.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;13(10):948. doi: 10.3390/bios13100948. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IoT in Radiology: Using Raspberry Pi to Automatically Log Telephone Calls in the Reading Room.J Digit Imaging. 2018 Jun;31(3):371-378. doi: 10.1007/s10278-018-0081-z. J Digit Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29725966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial for the Special Issue on 3D Printed Actuators.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;14(1):77. doi: 10.3390/mi14010077. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36677138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croft W.J. Under the Microscope A Brief History of Microscopy. World Scientific; Singapore: 2006.
-
- Murphy D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2002.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

