Expansion of Double-Negative T Cells in Patients before Liver Transplantation Correlates with Post-Transplant Infections
- PMID: 35743569
- PMCID: PMC9225480
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123502
Expansion of Double-Negative T Cells in Patients before Liver Transplantation Correlates with Post-Transplant Infections
Abstract
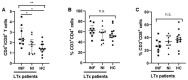
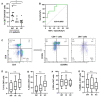
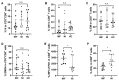
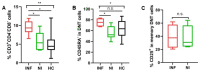
Liver transplantation (LTx) is currently the only effective therapy for patients with end-stage liver diseases, but post-transplant infection is a key issue for morbidity and mortality. In this study, we found that pre-transplant patients with an expansion of double-negative T (DNT) cells (CD3+CD4-CD8- T cells) had an increased incidence of infections within the first 6 months after LTx. These DNT cells also negatively correlated with their CD4/CD8 ratio. Compared to patients who had no infections after LTx, these DNT cells expressed more CD25, especially in the memory compartment. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis showed that the threshold area under the ROC curve of DNT cells which could be used to distinguish LTx patients with post-transplant infections from patients without infections after LTx was 0.8353 (95% CI: 0.6591-1.000). The cut-off for the pre-LTx DNT cell level was 11.35%. Although patients with post-transplant infections had decreased levels of CD4/CD8 T cells, CD8+ T cells in these patients were more exhausted, with higher PD-1 expression and lower IFNγ secretion. The increased levels of DNT cells in patients with post-transplant infections were still observed 2 weeks after LTx, with higher proportions of memory DNT cells. In conclusion, increased levels of DNT cells in pre-LTx patients may be valuable for the prognosis of post-transplant infections, especially within the first 6 months after LTx.
Keywords: T cell exhaustion; double negative T cells; immunosuppressive therapy; infections; liver transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of double-negative T cells in colorectal cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34645. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34645. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39114054 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased CD73+ Double-Negative T Cells and Elevated Level of Soluble CD73 Correlated With and Predicted Poor Immune Reconstitution in HIV-Infected Patients After Antiretroviral Therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 4;13:869286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869286. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35444646 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of alpha-1-fetoprotein (AFP) as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation.Clin Biochem. 2018 Feb;52:20-25. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Clin Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29054441
-
Nutrition therapy: Integral part of liver transplant care.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 28;22(4):1513-22. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1513. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26819518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single center experience of combined liver kidney transplantation.Clin Transplant. 2009 Dec;23 Suppl 21:102-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01146.x. Clin Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19930323 Review.
Cited by
-
Double-Negative T (DNT) Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 12;12(1):166. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010166. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

