O-GlcNAcylation: An Emerging Protein Modification Regulating the Hippo Pathway
- PMID: 35740678
- PMCID: PMC9221189
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14123013
O-GlcNAcylation: An Emerging Protein Modification Regulating the Hippo Pathway
Abstract
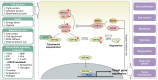
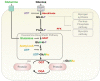
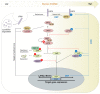
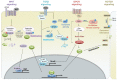
The balance between cellular proliferation and apoptosis and the regulation of cell differentiation must be established to maintain tissue homeostasis. These cellular responses involve the kinase cascade-mediated Hippo pathway as a crucial regulator. Hence, Hippo pathway dysregulation is implicated in diverse diseases, including cancer. O-GlcNAcylation is a non-canonical glycosylation that affects multiple signaling pathways through its interplay with phosphorylation in the nucleus and cytoplasm. An abnormal increase in the O-GlcNAcylation levels in various cancer cells is a potent factor in Hippo pathway dysregulation. Intriguingly, Hippo pathway dysregulation also disrupts O-GlcNAc homeostasis, leading to a persistent elevation of O-GlcNAcylation levels, which is potentially pathogenic in several diseases. Therefore, O-GlcNAcylation is gaining attention as a protein modification that regulates the Hippo pathway. This review presents a framework on how O-GlcNAcylation regulates the Hippo pathway and forms a self-perpetuating cycle with it. The pathological significance of this self-perpetuating cycle and clinical strategies for targeting O-GlcNAcylation that causes Hippo pathway dysregulation are also discussed.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; O-GlcNAcylation; cancer; cellular signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
O-GlcNAcylation on LATS2 disrupts the Hippo pathway by inhibiting its activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 23;117(25):14259-14269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913469117. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32513743 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Hippo-YAP Pathway by Glucose Sensor O-GlcNAcylation.Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 2;68(3):591-604.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.010. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 29100056
-
Feedback Regulation of O-GlcNAc Transferase through Translation Control to Maintain Intracellular O-GlcNAc Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;22(7):3463. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073463. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801653 Free PMC article.
-
Too sweet to resist: Control of immune cell function by O-GlcNAcylation.Cell Immunol. 2018 Nov;333:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.05.010. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Cell Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29887419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting O-GlcNAcylation to develop novel therapeutics.Mol Aspects Med. 2021 Jun;79:100885. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100885. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Mol Aspects Med. 2021. PMID: 32736806 Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of β-1, 3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases (B3GNTs) in human diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Mar 29;51(1):476. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09405-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38553573 Review.
-
MST2 methylation by PRMT5 inhibits Hippo signaling and promotes pancreatic cancer progression.EMBO J. 2023 Dec 1;42(23):e114558. doi: 10.15252/embj.2023114558. Epub 2023 Oct 31. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37905571 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

