A promising Prognostic risk model for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with immune-related genes
- PMID: 35739510
- PMCID: PMC9229885
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09755-2
A promising Prognostic risk model for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with immune-related genes
Abstract
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a third most common tumor of the urinary system. Nowadays, Immunotherapy is a hot topic in the treatment of solid tumors, especially for those tumors with pre-activated immune state.
Methods: In this study, we downloaded genomic and clinical data of RCC samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Four immune-related genetic signatures were used to predict the prognosis of RCC by Cox regression analysis. Then we established a prognostic risk model consisting of the genes most related to prognosis from four signatures to value prognosis of the RCC samples via Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival analysis. An independent data from International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) database were used to test the predictive stability of the model. Furthermore, we performed landscape analysis to assess the difference of gene mutant in the RCC samples from TCGA. Finally, we explored the correlation between the selected genes and the level of tumor immune infiltration via Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) platform.
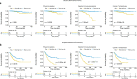
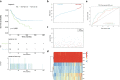
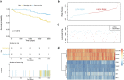
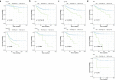
Results: We used four genetic signatures to construct prognostic risk models respectively and found that each of the models could divide the RCC samples into high- and low-risk groups with significantly different prognosis, especially in advanced RCC. A comprehensive prognostic risk model was constructed by 8 candidate genes from four signatures (HLA-B, HLA-A, HLA-DRA, IDO1, TAGAP, CIITA, PRF1 and CD8B) dividing the advanced RCC samples from TCGA database into high-risk and low-risk groups with a significant difference in cancer-specific survival (CSS). The stability of the model was verified by independent data from ICGC database. And the classification efficiency of the model was stable for the samples from different subgroups. Landscape analysis showed that mutation ratios of some genes were different between two risk groups. In addition, the expression levels of the selected genes were significantly correlated with the infiltration degree of immune cells in the advanced RCC.
Conclusions: Sum up, eight immune-related genes were screened in our study to construct prognostic risk model with great predictive value for the prognosis of advanced RCC, and the genes were associated with infiltrating immune cells in tumors which have potential to conduct personalized treatment for advanced RCC.
Keywords: Immunologic signature; Prognosis; RCC; Renal cell carcinoma; Tumor immunity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel nine-microRNA-based model to improve prognosis prediction of renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 12;22(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09322-9. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35279104 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Novel Immune-Related lncRNA Pair Signature with Prognostic Significance for Kidney Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2021 Sep 1;2021:8800358. doi: 10.1155/2021/8800358. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34512816 Free PMC article.
-
The JAK-STAT signaling-related signature serves as a prognostic and predictive biomarker for renal cell carcinoma immunotherapy.Gene. 2024 Nov 15;927:148719. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148719. Epub 2024 Jun 23. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38917875
-
Neopterin as a potential prognostic and predictive biomarker in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024 Jun;24(6):339-345. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2024.2341734. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38596831 Review.
-
Imaging Techniques to Determine Degree of Sarcopenia and Systemic Inflammation in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Curr Urol Rep. 2023 Jul;24(7):317-334. doi: 10.1007/s11934-023-01157-6. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Curr Urol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37036632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A promising natural killer cell-based model and a nomogram for the prognostic prediction of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 24;29(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01659-0. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38268058 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant Therapy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: End Points, Outcomes, and Risk Assessments.JCO Precis Oncol. 2023 Feb;7:e2200407. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00407. JCO Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36724413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in renal cell carcinoma progression and clinical therapy via targeting metabolic regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1122065. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1122065. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36969848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing a prognostic model of chromatin modulators and identifying potential drug candidates in renal clear cell patients.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 20;24(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05229-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36941564 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Validation of Survival-Specific Genes in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma Using a Customized Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Panel.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 25;16(11):2006. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112006. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA,Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2018; 68: 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Fernandez-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Kuusk T, Lam TB, Marconi L, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 Update. Eur Urol. 2019;75:799–810. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.011. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

