In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
- PMID: 35738174
- PMCID: PMC9212324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2022.06.008
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Abstract
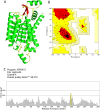
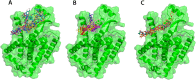
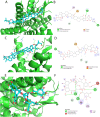
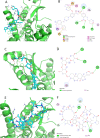
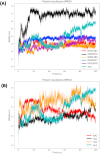
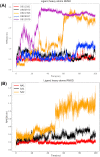
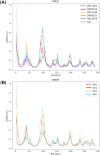
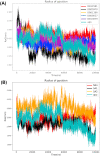
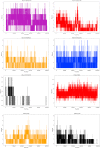
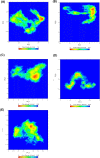
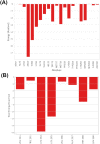
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were virtually screened, namely FDA-approved drugs (DrugBank), Northern African Natural Products Database (NANPDB) and South African Natural Compounds Database (SANCDB) with a total of 8158 compounds. Further validation for 9 candidates via molecular dynamics simulations for 100 ns recommended potential binders to the NSP6 binding site. The proposed candidates are recommended for biological testing to cease the rapidly growing pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Docking; DrugBank; Molecular dynamics; NSP6; Natural products.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


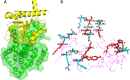

Similar articles
-
Insights into the biased activity of dextromethorphan and haloperidol towards SARS-CoV-2 NSP6: in silico binding mechanistic analysis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Dec;98(12):1659-1673. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01980-1. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32965508 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of natural products to block SARS-CoV-2 S-protein interaction with Neuropilin-1 receptor: A molecular dynamics simulation approach.Microb Pathog. 2022 Sep;170:105701. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105701. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35963279 Free PMC article.
-
Potential COVID-19 Therapies from Computational Repurposing of Drugs and Natural Products against the SARS-CoV-2 Helicase.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7704. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147704. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887049 Free PMC article.
-
Structure based Drug Designing Approaches in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Inhibitor Design.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(29):2396-2409. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221103091658. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36330617 Review.
-
An Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Potential Targets, Inhibitors, and Computational Insights to Enrich the Promising Treatment Strategies.Curr Microbiol. 2024 May 11;81(7):169. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03671-3. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38733424 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular insights into the inhibition mechanism of harringtonine against essential proteins associated with SARS-CoV-2 entry.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 15;240:124352. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124352. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37054859 Free PMC article.
-
Unleashing Nature's potential: a computational approach to discovering novel VEGFR-2 inhibitors from African natural compound using virtual screening, ADMET analysis, molecular dynamics, and MMPBSA calculations.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Sep 20;10:1227643. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1227643. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37800126 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a membrane-associated element (MAE) in the C-terminal region of SARS-CoV-2 nsp6 that is essential for viral replication.J Virol. 2024 May 14;98(5):e0034924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00349-24. Epub 2024 Apr 19. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38639488 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Targeting of Fascin Protein for Cancer Therapy: Benchmarking, Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Approaches.Molecules. 2023 Jan 29;28(3):1296. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031296. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770963 Free PMC article.
-
Using AlphaFold Predictions in Viral Research.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Apr 21;45(4):3705-3732. doi: 10.3390/cimb45040240. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37185764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham M.J., Murtola T., Schulz R., Páll S., Smith J.C., et al. GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. Software. 2015 1-2 19-25.
-
- Baell J.B., Holloway G.A. New substructure filters for removal of Pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010;53:2719–2740. - PubMed
-
- Belz G.G., Breithaupt-Grögler K., Osowski U. Treatment of congestive heart failure--current status of use of digitoxin. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2001;31(Suppl. 2):10–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

