Mechanisms Underlying Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Mislocalization in Epilepsy
- PMID: 35734218
- PMCID: PMC9207308
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.900588
Mechanisms Underlying Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Mislocalization in Epilepsy
Abstract
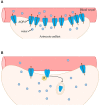
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder characterized by unprovoked seizures. Mechanisms underlying seizure activity have been intensely investigated. Alterations in astrocytic channels and transporters have shown to be a critical player in seizure generation and epileptogenesis. One key protein involved in such processes is the astrocyte water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4). Studies have revealed that perivascular AQP4 redistributes away from astrocyte endfeet and toward the neuropil in both clinical and preclinical studies. This subcellular mislocalization significantly impacts neuronal hyperexcitability and understanding how AQP4 becomes dysregulated in epilepsy is beginning to emerge. In this review, we evaluate the role of AQP4 dysregulation and mislocalization in epilepsy.
Keywords: aquaporin-4; astrocytes; epilepsy; seizures; subcellular localization.
Copyright © 2022 Szu and Binder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mislocalization of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsy Res. 2013 Jul;105(1-2):30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.01.006. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Epilepsy Res. 2013. PMID: 23357720
-
Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis.Exp Neurol. 2012 May;235(1):246-55. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.02.002. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22361023 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in epilepsy.Neuron Glia Biol. 2007 Nov;3(4):287-97. doi: 10.1017/S1740925X08000112. Neuron Glia Biol. 2007. PMID: 18634561
-
Aquaporin-4 and epilepsy.Glia. 2012 Aug;60(8):1203-14. doi: 10.1002/glia.22317. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Glia. 2012. PMID: 22378467 Review.
-
Mechanisms of astrocyte-mediated cerebral edema.Neurochem Res. 2015 Feb;40(2):317-28. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1374-3. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 24996934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Aquaporins in Epileptogenesis-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 25;24(15):11923. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511923. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-4 and Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 30;25(3):1672. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031672. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neurovascular Unit Dysfunction in the Molecular Mechanisms of Epileptogenesis and Targeted Therapy.Neurosci Bull. 2024 May;40(5):621-634. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01193-3. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 38564049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins: Gatekeepers of Fluid Dynamics in Traumatic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasudil attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in C57BL/6 mice through anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects: Possible role of aquaporin-4.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;17:372-381. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.10.004. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39534317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M., Otsuka T., Hurn P. D., Traystman R. J. F.-M., Froehner S. C., et al. . (2003). An α-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100, 2106–2111. 10.1073/pnas.0437946100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

