Sequential detection of hypochlorous acid and sulfur dioxide derivatives by a red-emitting fluorescent probe and bioimaging applications in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 35733666
- PMCID: PMC9135002
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra01048h
Sequential detection of hypochlorous acid and sulfur dioxide derivatives by a red-emitting fluorescent probe and bioimaging applications in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
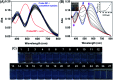
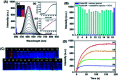
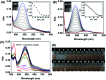
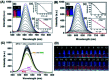
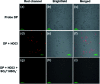
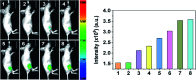
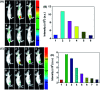
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and sulfur dioxide derivatives (SO3 2-/HSO3 -) play critical roles in complex signal transduction and oxidation pathways. Therefore, it is meaningful and valuable to detect both HOCl and SO2 derivatives in biosystems by a fluorescence imaging assay. In this work, we developed a red-emitting fluorescent probe (DP) by the condensation of malononitrile and phenothiazine derivatives through a C[double bond, length as m-dash]C double bond. DP was designed with a donor-π-acceptor (D-π-A) structure, which enables absorption and emission in the long wavelength region. In the presence of HOCl, specific oxidation of the thioether of phenothiazine in DP to a sulfoxide derivative (DP[double bond, length as m-dash]O) occurs, resulting in a hypochromic shift (572 nm to 482 nm) of the absorption spectra and "OFF-ON" response of the maximum emission at 608 nm. After the activation of the C[double bond, length as m-dash]C double bond by oxidation, DP[double bond, length as m-dash]O reacts specifically with SO3 2-/HSO3 - via a 1,4-nucleophilic addition reaction leading to a decrease in the intensity of the absorption and emission spectra, which enabled the realization of sequential detection of HOCl and SO3 2-/HSO3 - by a single fluorescent probe. The detection limits of DP for HOCl and SO3 2-/HSO3 - were calculated to be 81.3 nM and 70.8 nM/65.1 nm, respectively. The results of fluorescence microscopic imaging indicated that DP shows potential for the detection of intracellular HOCl and SO3 2-/HSO3 -. Using adult zebrafish and nude mice as live animal models, DP was successfully used for the fluorescence imaging of HOCl and SO3 2-/HSO3 - in vivo.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bifunctional near-infrared fluorescent probe for the selective detection of bisulfite and hypochlorous acid in food, water samples and in vivo.Anal Chim Acta. 2023 Oct 23;1279:341783. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.341783. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Anal Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 37827680
-
All-in-one: Accurate quantification, on-site detection, and bioimaging of sulfite using a colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe in vitro and in vivo.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Feb 15;424(Pt B):127229. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127229. Epub 2021 Sep 14. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 34653860
-
A highly sensitive ratiometric fluorescent probe for detecting HSO3-/SO32- and viscosity change based on FRET/TICT mechanism.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 May 29;1305:342588. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342588. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38677842
-
A Ratiometric and Colorimetric Hemicyanine Fluorescent Probe for Detection of SO2 Derivatives and Its Applications in Bioimaging.Molecules. 2019 Nov 5;24(21):4011. doi: 10.3390/molecules24214011. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31694349 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in the small-molecule fluorescent probes for the detection of sulfur dioxide derivatives (HSO3-/SO32-).Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Dec;145:42-60. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31525454 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

