Modulation of viral replication, apoptosis and antiviral response by induction and mutual regulation of EGR and AP-1 family genes during coronavirus infection
- PMID: 35727266
- PMCID: PMC9262369
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2093133
Modulation of viral replication, apoptosis and antiviral response by induction and mutual regulation of EGR and AP-1 family genes during coronavirus infection
Abstract
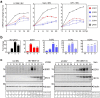
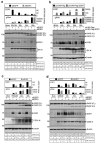
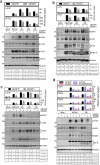
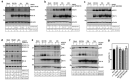
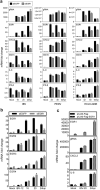
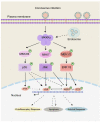
Coronaviruses have evolved a variety of strategies to exploit normal cellular processes and signalling pathways for their efficient reproduction in a generally hostile cellular environment. One immediate-early response gene (IEG) family, the AP-1 gene family, was previously shown to be activated by coronavirus infection. In this study, we report that another IEG family, the EGR family, is also activated in cells infected with four different coronaviruses in three genera, i.e. gammacoronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), alphacoronaviruses porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) and human coronavirus-229E (HCoV-229E), and betacoronavirus HCoV-OC43. Knockdown of EGR1 reduced the expression of cJUN and cFOS, and knockdown of cJUN and/or cFOS reduced the expression of EGR1, demonstrating that these two IEG families may be cross-activated and mutual regulated. Furthermore, ERK1/2 was identified as an upstream kinase, and JNK and p38 as inhibitors of EGR1 activation in coronavirus-infected cells. However, upregulation of EGR family genes, in particular EGR1, appears to play a differential role in regulating viral replication, apoptosis and antiviral response. EGR1 was shown to play a limited role in regulation of coronavirus replication, and an anti-apoptotic role in cells infected with IBV or PEDV, but not in cells infected with HCoV-229E. Upregulation of EGR1 may also play a differential role in the regulation of antiviral response against different coronaviruses. This study reveals a novel regulatory network shared by different coronaviruses in the immediate-early response of host cells to infection.
Keywords: AP-1; Coronavirus; EGR1; ERK1/2; apoptosis; cross-activation; cytokines; immediate-early genes.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gammacoronavirus Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Alphacoronavirus Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Exploit a Cell-Survival Strategy via Upregulation of cFOS to Promote Viral Replication.J Virol. 2021 Feb 15;95(4):e02107-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02107-20. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33239458 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the MKK3-p38-MK2-ZFP36 Axis by Coronavirus Infection Restricts the Upregulation of AU-Rich Element-Containing Transcripts in Proinflammatory Responses.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0208621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02086-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34985993 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the induction kinetics and antiviral functions of IRF1, ISG15 and ISG20 in cells infected with gammacoronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus.Virology. 2023 May;582:114-127. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2023.03.017. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Virology. 2023. PMID: 37058744 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus genome structure and replication.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;287:1-30. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26765-4_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15609507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2.Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3-11. Malays J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32342926 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress Relief by CAPE in ARPE-19 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3565. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043565. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834980 Free PMC article.
-
Role of early growth response 1 in inflammation-associated lung diseases.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):L143-L154. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00413.2022. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37401387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune response in COVID-19: single-cell multi-omics profile of NK lymphocytes in a clinical case series.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 15;22(1):496. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01867-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39407208 Free PMC article.
-
Human Coronavirus 229E Infection Inactivates Pyroptosis Executioner Gasdermin D but Ultimately Leads to Lytic Cell Death Partly Mediated by Gasdermin E.Viruses. 2024 Jun 1;16(6):898. doi: 10.3390/v16060898. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932190 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the role of EGR1 during viral infections.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1020220. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020220. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fung TS, Liu DX.. Human coronavirus: host-pathogen interaction. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2019;73:529–557. - PubMed
-
- Fung TS, Liu DX.. Similarities and dissimilarities of COVID-19 and other coronavirus diseases. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2021;75:19–47. - PubMed
-
- Healy S, Khan P, Davie JR.. Immediate early response genes and cell transformation. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;137(1):64–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
