Contribution of Helicobacter pylori to the Inflammatory Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency
- PMID: 35711410
- PMCID: PMC9193800
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.834137
Contribution of Helicobacter pylori to the Inflammatory Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency
Abstract
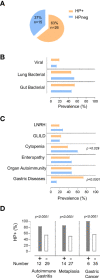
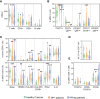
Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID), the most prevalent symptomatic primary immunodeficiency, is frequently associated with severe inflammatory complications that determine its morbidity and mortality. We hypothesize that Helicobacter pylori (HP), a very common worldwide infection, may contribute to the clinical and immune phenotype of CVID. We stratified 41 CVID patients into HP+ (n=26) and HPneg (n=15) groups, according to previous urease breath test and/or gastric biopsies, and compared their clinical manifestations and immune profile evaluated by flow cytometry. No genetic variants with known potential impact in HP infection were found upon WES/WGS. Gastric complications were significantly more frequent in HP+ patients. Importantly, the six CVID patients with gastric cancer were infected with HP. In contrast, a significantly higher frequency of cytopenias was observed in the HPneg. Moreover, HP+ did not feature higher prevalence of organ auto-immunity, as well as of lung, liver or intestinal inflammatory manifestations. We observed the same B-cell profiles in HP+ and HPneg groups, accompanied by marked CD4 and CD8 T-cell activation, increased IFNγ production, and contraction of naïve compartments. Notably, HP+ patients featured low CD25 despite preserved Foxp3 levels in CD4 T cells. Overall, HP impact in CVID inflammatory complications was mainly restricted to the gastric mucosa, contributing to increased incidence of early onset gastric cancer. Thus, early HP screening and eradication should be performed in all CVID patients irrespective of symptoms.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; common variable immunodeficiency (CVID); gastric cancer; inborn error of immunity (IEI); inflammatory CVID complications; primary immunodeficiency.
Copyright © 2022 Motta-Raymundo, Rosmaninho, Santos, Ferreira, Silva, Ferreira, Sousa and Silva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastric Cancer Is the Leading Cause of Death in Italian Adult Patients With Common Variable Immunodeficiency.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 5;9:2546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02546. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30455695 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysfunctional Immune System in Common Variable Immunodeficiency Increases the Susceptibility to Gastric Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jun 19;9(6):1498. doi: 10.3390/cells9061498. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32575504 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Cancer Screening in Common Variable Immunodeficiency.J Clin Immunol. 2018 Oct;38(7):768-777. doi: 10.1007/s10875-018-0546-3. Epub 2018 Sep 15. J Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30219982
-
Chemoprevention of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori eradication and its underlying mechanism.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;34(8):1287-1295. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14646. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30828872 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancerogenesis.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;60(3):3-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19826177 Review.
Cited by
-
Possible Role of Cytomegalovirus in Gastric Cancer Development and Recurrent Macrolide-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Common Variable Immunodeficiency: A Case Report and Literature Discussion.Microorganisms. 2024 May 27;12(6):1078. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061078. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equine common variable immunodeficiency: lessons from 100 clinical cases.Equine Vet Educ. 2024 Oct;36(10):543-554. doi: 10.1111/eve.13948. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Equine Vet Educ. 2024. PMID: 39555145
-
Decline of gastric cancer mortality in common variable immunodeficiency in the years 2018-2022.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 6;14:1231242. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1231242. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37868983 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding mutational hotspots in human disease through the gene modules governing thymic regulatory T cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1458581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458581. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483472 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical analysis of the effect of helicobacter pylori infection on immune function in children with peptic ulcer.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jul;40(6):1063-1066. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.6.7820. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38952501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berbers R-M, Drylewicz J, Ellerbroek PM, van Montfrans JM, Dalm VASH, van Hagen PM, et al. . Targeted Proteomics Reveals Inflammatory Pathways That Classify Immune Dysregulation in Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021) 41:362–73. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00908-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

