Evaluation of concurrent vaccinations with recombinant canarypox equine influenza virus and inactivated equine herpesvirus vaccines
- PMID: 35709134
- PMCID: PMC9184697
- DOI: 10.5187/jast.2022.e30
Evaluation of concurrent vaccinations with recombinant canarypox equine influenza virus and inactivated equine herpesvirus vaccines
Abstract
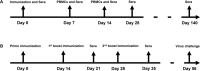
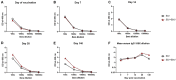
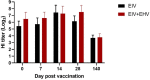
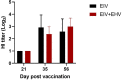
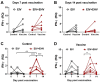
Despite vaccination, equine influenza virus (EIV) and equine herpesvirus (EHV) infections still cause highly contagious respiratory diseases in horses. Recently, concurrent vaccination with EIV and EHV was suggested as a new approach; however, there have been no reports of concurrent vaccination with recombinant canarypox EIV and inactivated EHV vaccines. In this study, we aimed to compare the EIV-specific immune responses induced by concurrent administrations of a recombinant canarypox EIV vaccine and an inactivated bivalent EHV vaccine with those induced by a single recombinant canarypox EIV vaccine in experimental horse and mouse models. Serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected from immunized animals after vaccination. EIV-specific serum antibody levels, serum hemagglutinin inhibition (HI) titers, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, HI assay, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Concurrent EIV and EHV vaccine administration significantly increased IFN-γ production, without compromising humoral responses. Our data demonstrate that concurrent vaccination with EIV and EHV vaccines can enhance EIV-specific cellular responses in horses.
Keywords: Concurrent vaccination; Equine herpes virus; Equine influenza virus; Immune response.
© Copyright 2022 Korean Society of Animal Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concurrent vaccination against equine influenza and equine herpesvirus - a practical approach.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2016 Sep;10(5):433-7. doi: 10.1111/irv.12396. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27169603 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Responses Against Equine Influenza Virus Induced by Concurrent and by Consecutive Use of an Inactivated Equine Influenza Virus Vaccine and a Modified Live Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 Vaccine in Thoroughbred Racehorses.J Equine Vet Sci. 2020 Nov;94:103221. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2020.103221. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Equine Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33077093
-
Antibody and IFN-gamma responses induced by a recombinant canarypox vaccine and challenge infection with equine influenza virus.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2006 Aug 15;112(3-4):225-33. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2006.02.007. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2006. PMID: 16621023
-
How to Meet the Last OIE Expert Surveillance Panel Recommendations on Equine Influenza (EI) Vaccine Composition: A Review of the Process Required for the Recombinant Canarypox-Based EI Vaccine.Pathogens. 2016 Nov 25;5(4):64. doi: 10.3390/pathogens5040064. Pathogens. 2016. PMID: 27897990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equine Influenza Virus and Vaccines.Viruses. 2021 Aug 20;13(8):1657. doi: 10.3390/v13081657. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452521 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro effects of monophosphoryl lipid A and Poly I:C combination on equine cells.J Vet Sci. 2023 May;24(3):e37. doi: 10.4142/jvs.23007. J Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37271505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heldens JGM, Van De Wouw JCA, Van Loon AAWM. An updated equine influenza vaccine and an equine influenza-herpesvirus combination vaccine containing an immunostim adjuvant provoke equal antibody levels in young foals throughout the primary vaccination course. Vet J. 2002;164:288–91. doi: 10.1053/tvjl.2002.0712. - DOI - PubMed
-
- OIE World Organisation for Animal Health . OIE Terrestrial Manual 2019. Paris: OIE World Organisation for Animal Health; 2019. Equine influenza (infection with equine influenza virus)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

