SFPQ Promotes Lung Cancer Malignancy via Regulation of CD44 v6 Expression
- PMID: 35707369
- PMCID: PMC9190464
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.862250
SFPQ Promotes Lung Cancer Malignancy via Regulation of CD44 v6 Expression
Abstract
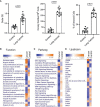
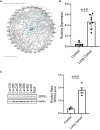
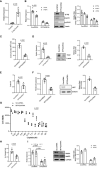
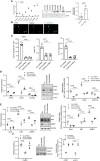
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) contribute to tumor pathogenesis and elicit antitumor immune responses in tumor microenvironments. Nuclear proteins might be the main players in these processes. In the current study, combining spatial proteomics with ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) in lung non-small cell (NSC) cancer MSCs, we identify a key nuclear protein regulator, SFPQ (Splicing Factor Proline and Glutamine Rich), which is overexpressed in lung cancer MSCs and functions to promote MSCs proliferation, chemical resistance, and invasion. Mechanistically, the knockdown of SFPQ reduces CD44v6 expression to inhibit lung cancer MSCs stemness, proliferation in vitro, and metastasis in vivo. The data indicates that SFPQ may be a potential therapeutic target for limiting growth, chemotherapy resistance, and metastasis of lung cancer.
Keywords: CD44v6; SFPQ; ingenuity pathway analysis; lung non-small cell (NSC) cancer; mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); nuclear fraction; quantitative proteomics.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Yang, Jacobson, Gilbertsen, Smith, Higgins, Guerrero, Xia, Henke and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA NEAT1 Recruits SFPQ to Regulate MITF Splicing and Control RPE Cell Proliferation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Nov 1;62(14):18. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.14.18. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34787639 Free PMC article.
-
The splicing factor proline and glutamine rich promotes the growth of osteosarcoma via the c-Myc signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;13(6):2488-2503. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37424803 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer through binding to SFPQ and releasing oncogene PTBP2 from SFPQ/PTBP2 complex.Br J Cancer. 2014 Aug 12;111(4):736-48. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.383. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25025966 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of the RNA-Binding Protein SFPQ in Neuronal Function and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7151. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197151. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-edged sword of mesenchymal stem cells: Cancer-promoting versus therapeutic potential.Cancer Sci. 2017 Oct;108(10):1939-1946. doi: 10.1111/cas.13334. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28756624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SFPQ and Its Isoform as Potential Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;24(15):12500. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512500. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569873 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6, STn & O-GD2: promising tumor associated antigens paving the way for new targeted cancer therapies.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 3;14:1272681. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272681. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37854601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins regulating the CD44 alternative splicing.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 1;10:1326148. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1326148. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38106992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Paraspeckles Expression in Osteosarcoma Tissues.Cancer Inform. 2022 Dec 5;21:11769351221140101. doi: 10.1177/11769351221140101. eCollection 2022. Cancer Inform. 2022. PMID: 36507075 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial proteomics: unveiling the multidimensional landscape of protein localization in human diseases.Proteome Sci. 2024 Sep 20;22(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12953-024-00231-2. Proteome Sci. 2024. PMID: 39304896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vianello F, Villanova F, Tisato V, Lymperi S, Ho KK, Gomes AR, et al. . Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Non-Selectively Protect Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells From Imatinib-Induced Apoptosis via the CXCR4/CXCL12 Axis. Haematologica (2010) 95:1081–9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.017178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Ameri W, Ahmed I, Al-Dasim FM, Ali Mohamoud Y, Al-Azwani IK, Malek JA, et al. . Cell Type-Specific TGF-Beta Mediated EMT in 3D and 2D Models and Its Reversal by TGF-Beta Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20(14):3568. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143568 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Csermely P, Hodsagi J, Korcsmaros T, Modos D, Perez-Lopez AR, Szalay K, et al. . Cancer Stem Cells Display Extremely Large Evolvability: Alternating Plastic and Rigid Networks as a Potential Mechanism: Network Models, Novel Therapeutic Target Strategies, and the Contributions of Hypoxia, Inflammation and Cellular Senescence. Semin Cancer Biol (2015) 30:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.12.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Contreras HR, Lopez-Moncada F, Castellon EA. Cancer Stem Cell and Mesenchymal Cell Cooperative Actions in Metastasis Progression and Hormone Resistance in Prostate Cancer: Potential Role of Androgen and Gonadotropinreleasing Hormone Receptors (Review). Int J Oncol (2020) 56:1075–82. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

