Nanoscale bioconjugates: A review of the structural attributes of drug-loaded nanocarrier conjugates for selective cancer therapy
- PMID: 35706949
- PMCID: PMC9189039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09577
Nanoscale bioconjugates: A review of the structural attributes of drug-loaded nanocarrier conjugates for selective cancer therapy
Abstract
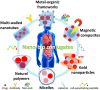
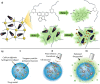
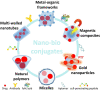
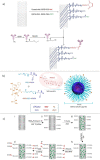
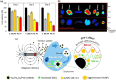
Nanobioconjugates are nanoscale drug delivery vehicles that have been conjugated to or decorated with biologically active targeting ligands. These targeting ligands can be antibodies, peptides, aptamers, or small molecules such as vitamins or hormones. Most research studies in this field have been devoted to targeting cancer. Moreover, the nanostructures can be designed with an additional level of targeting by being designed to be stimulus-responsive or "smart" by a judicious choice of materials to be incorporated into the hybrid nanostructures. This stimulus could be an acidic pH, raised temperature, enzyme, ultrasound, redox potential, an externally applied magnetic field, or laser irradiation. In this case, the smart capability can increase the accumulation at the tumor site or the on-demand drug release, while the ligand ensures selective binding to the tumor cells. The present review highlights some interesting studies classified according to the nanostructure material. These materials include natural substances (polysaccharides), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (and halloysite nanotubes), metal-organic frameworks and covalent-organic frameworks, metal nanoparticles (gold and silver), and polymeric micelles.
Keywords: Biotechnology; High-tech nanostructures; Ligands for molecular recognition; Nanotechnology; Synergistic therapeutic effects; Targeted cancer therapy.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author MRH declares the following potential conflicts of interest: Scientific Advisory Boards: Transdermal Cap Inc, Cleveland, OH; BeWell Global Inc, Wan Chai, Hong Kong; Hologenix Inc. Santa Monica, CA; LumiThera Inc, Poulsbo, WA; Vielight, Toronto, Canada; Bright Photomedicine, Sao Paulo, Brazil; Quantum Dynamics LLC, Cambridge, MA; Global Photon Inc, Bee Cave, TX; Medical Coherence, Boston MA; NeuroThera, Newark DE; JOOVV Inc, Minneapolis-St. Paul MN; AIRx Medical, Pleasanton CA; FIR Industries, Inc. Ramsey, NJ; UVLRx Therapeutics, Oldsmar, FL; Ultralux UV Inc, Lansing MI; Illumiheal & Petthera, Shoreline, WA; MB Lasertherapy, Houston, TX; ARRC LED, San Clemente, CA; Varuna Biomedical Corp. Incline Village, NV; Niraxx Light Therapeutics, Inc, Boston, MA. Consulting; Lexington Int, Boca Raton, FL; USHIO Corp, Japan; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany; Philips Electronics Nederland B.V. Eindhoven, Netherlands; Johnson & Johnson Inc, Philadelphia, PA; SanofiAventis Deutschland GmbH, Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Stockholdings: Global Photon Inc, Bee Cave, TX; Mitonix, Newark, DE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasmonic photothermal release of docetaxel by gold nanoparticles incorporated onto halloysite nanotubes with conjugated 2D8-E3 antibodies for selective cancer therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Aug 11;19(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00982-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34380469 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in cancer therapy: Stimuli-responsive and biomimetic nanocomposites in targeted delivery, phototherapy and diagnosis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Mar;260(Pt 2):129391. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129391. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38242413 Review.
-
pH-sensitive nanocarrier based on gold/silver core-shell nanoparticles decorated multi-walled carbon manotubes for tracing drug release in living cells.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Jan 15;75:446-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26360244
-
Smart Nanocarriers as an Emerging Platform for Cancer Therapy: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Dec 27;27(1):146. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010146. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-Mediated Cancer Therapeutics Delivery using Micelles and Liposomes: A Review.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021;16(4):498-520. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666210706155110. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34911412 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-functionalized MOFs and AI-driven strategies for early cancer diagnosis and therapeutics.Biotechnol Lett. 2024 Feb;46(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s10529-023-03454-z. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Biotechnol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38155321 Review.
-
A diselenobis-functionalized magnetic catalyst based on iron oxide/silica nanoparticles suggested for amidation reactions.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 1;12(1):14865. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19030-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36050366 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous Lymphoma and Antibody-Directed Therapies.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(1):21. doi: 10.3390/antib12010021. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36975368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmonic porous micro- and nano-materials based on Au/Ag nanostructures developed for photothermal cancer therapy: challenges in clinicalization.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Nov 27;5(24):6768-6786. doi: 10.1039/d3na00763d. eCollection 2023 Dec 5. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 38059020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What is the Reason That the Pharmacological Future of Chemotherapeutics in the Treatment of Lung Cancer Could Be Most Closely Related to Nanostructures? Platinum Drugs in Therapy of Non-Small and Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Unexpected, Possible Interactions. The Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 14;19:9503-9547. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S469217. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39296940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Findik F. Nanomaterials and their applications. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2021;9:62–75.
-
- Abid N., Khan A.M., Shujait S., Chaudhary K., Ikram M., Imran M., Haider J., Khan M., Khan Q., Maqbool M. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021 - PubMed
-
- Baig N., Kammakakam I., Falath W. Nanomaterials: a review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. adv. 2021;2:1821–1871.
-
- Doustkhah E., Farajzadeh M., Mohtasham H., Habeeb J., Rostamnia S. Exfoliated graphene-based 2D materials: synthesis and catalytic behaviors. Handbook Graphene Set. 2019;1:529–558.
-
- Ghafuri H., Ganjali F., Hanifehnejad P. Cu. BTC MOF as a novel and efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 1, 8-dioxo-octa-hydro xanthene. Chem. Proc. 2020;3:2.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

