Development and Validation of an HPLC-UV Method for the Quantification of 4'-Hydroxydiclofenac Using Salicylic Acid: Future Applications for Measurement of In Vitro Drug-Drug Interaction in Rat Liver Microsomes
- PMID: 35684519
- PMCID: PMC9182407
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27113587
Development and Validation of an HPLC-UV Method for the Quantification of 4'-Hydroxydiclofenac Using Salicylic Acid: Future Applications for Measurement of In Vitro Drug-Drug Interaction in Rat Liver Microsomes
Abstract
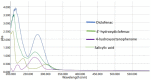
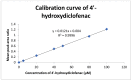
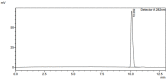
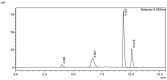
Salicylic acid is a key compound in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that has been recently used for preventing the risk of hospitalization and death among COVID-19 patients and in preventing colorectal cancer (CRC) by suppressing two key proteins. Understanding drug−drug interaction pathways prevent the occurrence of adverse drug reactions in clinical trials. Drug−drug interactions can result in the variation of the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic of the drug. Inhibition of the Cytochrome P450 enzyme activity leads to the withdrawal of the drug from the market. The aim of this paper was to develop and validate an HPLC-UV method for the quantification of 4′-hydroxydiclofenac as a CYP2C9 metabolite using salicylic acid as an inhibitor in rat liver microsomes. A CYP2C9 assay was developed and validated on the reversed phase C18 column (SUPELCO 25 cm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) using a low-pressure gradient elution programming at T = 30 °C, a wavelength of 282 nm, and a flow rate of 1 mL/min. 4′-hydroxydiclofenac demonstrated a good linearity (R2 > 0.99), good reproducibility, low detection, and quantitation limit, and the inter and intra-day precision met the ICH guidelines (<15%). 4′-hydroxydiclofenac was stable for three days and showed an acceptable accuracy and recovery (80−120%) within the ICH guidelines in a rat liver microsome sample. This method will be beneficial for future applications of the in vitro inhibitory effect of salicylic acid on the CYP2C9 enzyme activity in rat microsomes and the in vivo administration of salicylic acid in clinical trials.
Keywords: HPLC-UV; drug–drug interaction; method development; salicylic acid; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise, for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of an HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Metabolic Reaction Products Catalysed by CYP2E1 Enzyme Activity: Inhibitory Effect of Cytochrome P450 Enzyme CYP2E1 by Salicylic Acid in Rat Liver Microsomes.Molecules. 2020 Feb 19;25(4):932. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040932. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32093091 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of an HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Metabolic Reaction Products Catalysed by CYP2C11 Enzymes in Rat Liver Microsomes: In Vitro Inhibitory Effect of Salicylic Acid on CYP2C11 Enzyme.Molecules. 2019 Nov 25;24(23):4294. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234294. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31775347 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Assessment of UGT2B17 Inhibition by Salicylic Acid in Human Supersomes In Vitro.Molecules. 2021 Jul 21;26(15):4410. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154410. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361561 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous quantitation of etoricoxib, salicylic acid, valdecoxib, ketoprofen, nimesulide and celecoxib in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection.Biomed Chromatogr. 2006 Jan;20(1):125-32. doi: 10.1002/bmc.539. Biomed Chromatogr. 2006. PMID: 16013036
-
Development and Validation of a Novel HPLC Method to Analyse Metabolic Reaction Products Catalysed by the CYP3A2 Isoform: In Vitro Inhibition of CYP3A2 Enzyme Activity by Aspirin (Drugs Often Used Together in COVID-19 Treatment).Molecules. 2022 Jan 29;27(3):927. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030927. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164195 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

