Pathogenic Impact of α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Its Kinases in α-Synucleinopathies
- PMID: 35682892
- PMCID: PMC9181156
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116216
Pathogenic Impact of α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Its Kinases in α-Synucleinopathies
Abstract
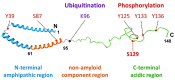
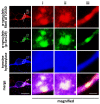
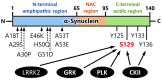
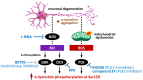
α-Synuclein is a protein with a molecular weight of 14.5 kDa and consists of 140 amino acids encoded by the SNCA gene. Missense mutations and gene duplications in the SNCA gene cause hereditary Parkinson's disease. Highly phosphorylated and abnormally aggregated α-synuclein is a major component of Lewy bodies found in neuronal cells of patients with sporadic Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and glial cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in oligodendrocytes with multiple system atrophy. Aggregated α-synuclein is cytotoxic and plays a central role in the pathogenesis of the above-mentioned synucleinopathies. In a healthy brain, most α-synuclein is unphosphorylated; however, more than 90% of abnormally aggregated α-synuclein in Lewy bodies of patients with Parkinson's disease is phosphorylated at Ser129, which is presumed to be of pathological significance. Several kinases catalyze Ser129 phosphorylation, but the role of phosphorylation enzymes in disease pathogenesis and their relationship to cellular toxicity from phosphorylation are not fully understood in α-synucleinopathy. Consequently, this review focuses on the pathogenic impact of α-synuclein phosphorylation and its kinases during the neurodegeneration process in α-synucleinopathy.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; dementia with Lewy bodies; multiple system atrophy; phosphorylation; α-synuclein; α-synucleinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of phosphorylation in synucleinopathies: focus on Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Aug;9(4):471-81. doi: 10.2174/187152710791556140. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20522010 Review.
-
Phosphorylated NUB1 distinguishes α-synuclein in Lewy bodies from that in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy.Brain Pathol. 2019 Nov;29(6):803-812. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12728. Epub 2019 May 17. Brain Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31006160 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in Synucleinopathy: The Overwhelmed and Defective Machinery.Cells. 2019 Jun 9;8(6):565. doi: 10.3390/cells8060565. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31181865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Dec 18;16(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00501-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34922583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological biochemistry of alpha-synucleinopathy.Neuropathology. 2007 Oct;27(5):474-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2007.00785.x. Neuropathology. 2007. Retraction in: Neuropathology. 2012 Jun;32(3):318. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2012.01313.x. PMID: 18018483 Retracted.
Cited by
-
α-Synuclein seeding amplification assays for diagnosing synucleinopathies: an innovative tool in clinical implementation.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 21;13(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00449-2. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39574205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How phosphorylation impacts intrinsically disordered proteins and their function.Essays Biochem. 2022 Dec 16;66(7):901-913. doi: 10.1042/EBC20220060. Essays Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36350035 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein in synaptic function and dysfunction.Trends Neurosci. 2023 Feb;46(2):153-166. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Trends Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36567199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Technologies Unraveling the Significance of Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) as Crucial Players in Neurodegeneration.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 16;14(1):118. doi: 10.3390/biom14010118. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38254718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of proteins secreted by glial progenitor cells derived from human iPSCs.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Aug 6;18:1449063. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1449063. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39165834 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

