Molecular Basis of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/19 Signaling Axis
- PMID: 35682726
- PMCID: PMC9181207
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116046
Molecular Basis of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/19 Signaling Axis
Abstract
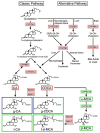
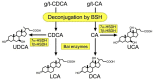
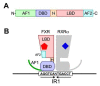
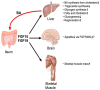
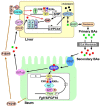
Bile acids (BAs) are a group of amphiphilic molecules consisting of a rigid steroid core attached to a hydroxyl group with a varying number, position, and orientation, and a hydrophilic side chain. While BAs act as detergents to solubilize lipophilic nutrients in the small intestine during digestion and absorption, they also act as hormones. Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a nuclear receptor that forms a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor α (RXRα), is activated by BAs in the enterohepatic circulation reabsorbed via transporters in the ileum and the colon, and plays a critical role in regulating gene expression involved in cholesterol, BA, and lipid metabolism in the liver. The FXR/RXRα heterodimer also exists in the distal ileum and regulates production of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 15/FGF19, a hormone traveling via the enterohepatic circulation that activates hepatic FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4)-β-klotho receptor complex and regulates gene expression involved in cholesterol, BA, and lipid metabolism, as well as those regulating cell proliferation. Agonists for FXR and analogs for FGF15/19 are currently recognized as a promising therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome and cholestatic diseases.
Keywords: bile acid; farnesoid X receptor; fibroblast growth factor 15/19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in the Digestive, Metabolic and Therapeutic Effects of Farnesoid X Receptor and Fibroblast Growth Factor 19: From Cholesterol to Bile Acid Signaling.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 22;14(23):4950. doi: 10.3390/nu14234950. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36500979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile Acids as Hormones: The FXR-FGF15/19 Pathway.Dig Dis. 2015;33(3):327-31. doi: 10.1159/000371670. Epub 2015 May 27. Dig Dis. 2015. PMID: 26045265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in Enterohepatic Fgf15 Signaling and Changes in Bile Acid Composition Depend on Localization of Murine Intestinal Inflammation.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016 Oct;22(10):2382-9. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000879. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016. PMID: 27580383
-
Hepatic cholesterol accumulation ascribed to the activation of ileum Fxr-Fgf15 pathway inhibiting hepatic Cyp7a1 in high-fat diet-induced obesity rats.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;232:116638. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116638. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288013
-
FXR Primes the Liver for Intestinal FGF15 Signaling by Transient Induction of β-Klotho.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Jan;30(1):92-103. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1226. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26505219 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Review: Cytochrome P450 in Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Apr 1;17:1511-1521. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S449494. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38586542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of the gut microbiota-bile acid-FGF19 axis in patients with atrial fibrillation.Cell Prolif. 2023 Nov;56(11):e13488. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13488. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 37186335 Free PMC article.
-
The supplementation of the multi-strain probiotics WHHPRO™ alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic symptoms in rats via gut-liver axis.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 11;10:1324691. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1324691. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38274203 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the power of microenvironment in liver regeneration: an in-depth overview.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 13;14:1332190. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1332190. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38152656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of FXR agonist GW4064 in the treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in rats.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 7;12(1):18873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23539-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36344586 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

