C2orf40 inhibits metastasis and regulates chemo-resistance and radio-resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by influencing cell cycle and activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 35676661
- PMCID: PMC9175486
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03446-z
C2orf40 inhibits metastasis and regulates chemo-resistance and radio-resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by influencing cell cycle and activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignant tumor of epithelial origin in head and neck with high incidence rate in Southern China. C2orf40 has been identified as a tumor suppressor gene in many cancers. However, the roles of C2orf40 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma has not been studied.
Methods: In this study, a bioinformatics analysis was performed to identify the differentially expressed genes in NPC. The quantitative methylation levels was detected using pyrosequencing. qRT-PCR, western blotting, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence were used to detect the expression level of related RNA and proteins. Cell proliferation was detected using CCK-8 assay, and colony formation capability was detected using colony formation assays. Cell migration and invasion were analyzed using wound-healing and Transwell assays, respectively. The apoptosis level of cells was assessed using TUNEL staining. Endogenous DNA damage and repair were assessed by the comet assay. Cell cycle analyses carried out by flow cytometry. Finally, We used a xenograft nude mouse to verify the roles of C2orf40 in chemoresistance and radioresistance in vivo.
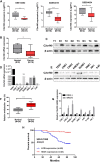
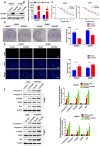
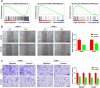
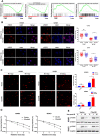
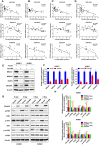
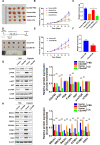
Results: We found that the C2orf40 expression was significantly downregulated in NPC tissues and inversely associated with a poor prognosis. In vivo and in vitro functional experiments confirmed that overexpression of C2orf40 significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of NPC cells, and promoted their sensitivity to radiotherapy and chemotherapy of NPC cells. Mechanically, the expression level of C2orf40 was negatively correlated with the expression levels of CCNE1 and CDK1. Overexpression of C2orf40 induced cell cycle arrest of NPC cells at G/M phase. In addition, C2orf40 can down-regulated the expression levels of homologous recombination-related proteins (BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51, and CDC25A) and inhibited the activity of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: The results clarified the biological functions and mechanisms of C2orf40, as a tumor suppressor gene, in NPC, and provided a potential molecular target for improving the sensitivity of NPC to radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Keywords: C2orf40; Metastasis; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway; Prognosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
APLNR is involved in ATRA-induced growth inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and may suppress EMT through PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling.FASEB J. 2019 Nov;33(11):11959-11972. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802416RR. Epub 2019 Aug 13. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31408612
-
Saucerneol attenuates nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation and metastasis through selectively targeting Grp94.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul;101:154133. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154133. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35504052
-
Chloroform extract from Sophora Tonkinensis Gagnep. inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion and promote apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by silencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113879. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113879. Epub 2021 Jan 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33524509
-
Regulatory role of miRNAs in nasopharyngeal cancer involving PTEN/PI3K/AKT, TGFβ/SMAD, RAS/MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin and pRB-E2F signaling pathways: A review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Mar;42(2):e3945. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3945. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38362935 Review.
-
The Roles of mTOR Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: From Pathogenesis to Therapy.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024;17:e18761429293675. doi: 10.2174/0118761429293675240709061332. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38988161 Review.
Cited by
-
Esophageal cancer-related gene 4 inhibits gastric cancer growth and metastasis by upregulating Krüppel-like factor 2 expression.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Feb 28;11(4):176. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-139. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36923086 Free PMC article.
-
Small biomarkers with massive impacts: PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling and microRNA crosstalk regulate nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Biomark Res. 2022 Jul 26;10(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00397-x. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 35883139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FBXW7 attenuates tumor drug resistance and enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 14;13:1147239. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1147239. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36998461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GSTM3 enhances radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting radiation-induced ferroptosis through USP14/FASN axis and GPX4.Br J Cancer. 2024 Mar;130(5):755-768. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02574-1. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38228715 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of diagnostic and prognostic models based on gene signatures of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by machine learning methods.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 May 31;12(5):1254-1269. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2700. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37304552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang XR, Li YQ, Liang SB, Jiang W, Liu F, Ge WX, et al. Development and validation of a gene expression-based signature to predict distant metastasis in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:382–393. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30080-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

