Involvement of Cdkal1 in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and microvascular diabetic complications: a review
- PMID: 35673487
- PMCID: PMC9167393
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00953-6
Involvement of Cdkal1 in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and microvascular diabetic complications: a review
Abstract
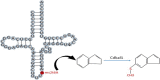
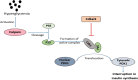
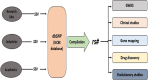
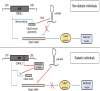
Diabetes Mellitus, being a polygenic disorder, have a set of risk genes involved in the onset of the insulin resistance, obesity and impaired insulin synthesis. Recent genome wide association studies (GWAS) shows the intimacy of CDK5 regulatory subunit Associated protein 1-Like 1 (Cdkal1) with the pathophysiology of the diabetes mellitus and its complications, although the exact molecular relation is still unknown. In this short review, we have summarized all the diverse biological roles of Cdkal1 in relation to the onset of diabetes mellitus. Variations in the Cdkal1 transcript are responsible for the accumulation of misfolded insulin and thus generating oxidative and ER stress in the pancreatic β-cells, leading to their destruction. Recent studies have shown that Cdkal1 has an intrinsic thiomethyl transferase activity, which is essential for proper posttranslational processing of pre-proinsulin to produce mature insulin. Moreover, Cdkal1 has also been claimed as an endogenous inhibitor of cdk5, which prevents the cdk5-induced interruption in insulin synthesis through PDX1 translocation from nucleus to cytosol. Recent clinical studies have identified the risk single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of Cdkal1 as one of the root causes for the onset of diabetic complications. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first comprehensive review which elaborates most of the potential Cdkal1-dependent molecular mechanisms studied yet. In this review, we present a compiled and concise summary about all the diverse roles of Cdkal1 in the context of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications. This review will be helpful to target Cdkal1 as a potential option for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in future.
Keywords: Cdkal1; Diabetes mellitus; Inflammation; Microvascular complications; SNPs; β cell regeneration.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional loss of Cdkal1, a novel tRNA modification enzyme, causes the development of type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2011;58(10):819-25. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej11-0099. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Endocr J. 2011. PMID: 21908934 Review.
-
The carriage of risk variants of CDKAL1 impairs beta-cell function in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients and reduces response to non-sulfonylurea and sulfonylurea agonists of the pancreatic KATP channel.Acta Diabetol. 2011 Sep;48(3):227-35. doi: 10.1007/s00592-011-0299-4. Epub 2011 May 25. Acta Diabetol. 2011. PMID: 21611789
-
CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1-like 1 (CDKAL1) is a tail-anchored protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of insulinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 7;287(50):41808-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.376558. Epub 2012 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23048041 Free PMC article.
-
Deficit of tRNA(Lys) modification by Cdkal1 causes the development of type 2 diabetes in mice.J Clin Invest. 2011 Sep;121(9):3598-608. doi: 10.1172/JCI58056. Epub 2011 Aug 15. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21841312 Free PMC article.
-
Different Associations Between CDKAL1 Variants and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Susceptibility: A Meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 5;12:783078. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.783078. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35069684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of Polymorphisms in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 7;25(4):2039. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042039. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lost pigs of Angola: Whole genome sequencing reveals unique regions of selection with emphasis on metabolism and feed efficiency.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 24;13:1003069. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1003069. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36353101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Who. c2020. World Health Organization. [Online]. [5 July 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
-
- Watanabe S, Wei FY, Tomizawa K. Functional characterization of Cdkal1, a risk factor of type 2 diabetes, and the translational opportunities. Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 2013;10(2):e65–e69. doi: 10.1016/j.ddmod.2012.12.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

