Targeting protein phosphatases for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases: From signaling to therapy
- PMID: 35665742
- PMCID: PMC9166240
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01038-3
Targeting protein phosphatases for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases: From signaling to therapy
Abstract
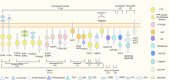
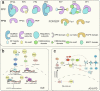
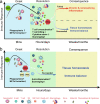
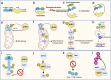
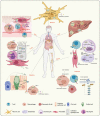
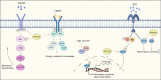
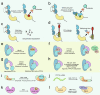
Inflammation is the common pathological basis of autoimmune diseases, metabolic diseases, malignant tumors, and other major chronic diseases. Inflammation plays an important role in tissue homeostasis. On one hand, inflammation can sense changes in the tissue environment, induce imbalance of tissue homeostasis, and cause tissue damage. On the other hand, inflammation can also initiate tissue damage repair and maintain normal tissue function by resolving injury and restoring homeostasis. These opposing functions emphasize the significance of accurate regulation of inflammatory homeostasis to ameliorate inflammation-related diseases. Potential mechanisms involve protein phosphorylation modifications by kinases and phosphatases, which have a crucial role in inflammatory homeostasis. The mechanisms by which many kinases resolve inflammation have been well reviewed, whereas a systematic summary of the functions of protein phosphatases in regulating inflammatory homeostasis is lacking. The molecular knowledge of protein phosphatases, and especially the unique biochemical traits of each family member, will be of critical importance for developing drugs that target phosphatases. Here, we provide a comprehensive summary of the structure, the "double-edged sword" function, and the extensive signaling pathways of all protein phosphatases in inflammation-related diseases, as well as their potential inhibitors or activators that can be used in therapeutic interventions in preclinical or clinical trials. We provide an integrated perspective on the current understanding of all the protein phosphatases associated with inflammation-related diseases, with the aim of facilitating the development of drugs that target protein phosphatases for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting Protein Phosphatases for the Treatment of Chronic Liver Disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(3):171-189. doi: 10.2174/0113894501278886231221092522. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38213163 Review.
-
Zinc in Regulating Protein Kinases and Phosphatases in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 4;12(6):785. doi: 10.3390/biom12060785. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of redox signaling, protein phosphatases and histone acetylation in the inflammatory cascade in acute pancreatitis. Therapeutic implications.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2010 Jun;9(2):97-108. doi: 10.2174/187152810791292773. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20361855 Review.
-
The emerging roles of phosphatases in Hedgehog pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Sep 20;15(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0191-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28931407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatases in plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1306:25-46. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2648-0_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25930691 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid hormone T3 induces Fyn modification and modulates palmitoyltransferase gene expression through αvβ3 integrin receptor in PC12 cells during hypoxia.Transl Neurosci. 2024 Aug 7;15(1):20220347. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0347. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39118829 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-specificity phosphatases 22-deficient T cells contribute to the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis.BMC Med. 2023 Feb 10;21(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02745-6. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 36765305 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inhibition of PTPN22 is a novel approach to alleviate osteogenic responses in aortic valve interstitial cells and aortic valve lesions in mice.BMC Med. 2023 Jul 13;21(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02888-6. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37443055 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a selective TC-PTP degrader for cancer immunotherapy.Chem Sci. 2023 Oct 24;14(44):12606-12614. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04541b. eCollection 2023 Nov 15. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38020389 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivity Profiling of Daedaleopsis confragosa (Bolton) J. Schröt. 1888: Implications for Its Possible Application in Enhancing Women's Reproductive Health.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 8;17(5):600. doi: 10.3390/ph17050600. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794170 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

