Distribution of human papillomavirus genotypes in suspected women cytological specimens from Tehran, Iran
- PMID: 35664716
- PMCID: PMC9085539
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v14i1.8812
Distribution of human papillomavirus genotypes in suspected women cytological specimens from Tehran, Iran
Abstract
Background and objectives: The human papillomavirus (HPV) is associated with more than 70% of the cervical neoplasm. The current study aims to evaluate the distribution of HPV genotypes in suspected women cytological specimens from Tehran, Iran.
Materials and methods: In the current cross-sectional study, HPV genotype prevalence was investigated in 433 subject women. DNA extraction was performed by High Pure Viral Nucleic Acid kit. A semi-automatically hybriSpot 24™ (HS24) setting was used for HPV typing and data interpreted by hybriSoft™ software according to instructions.
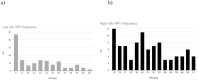
Results: Pathologic data showed 181 (41.8%) had non-malignant lesions, 212 (49%) had inflammation and 40 (9.2%) reported LSIL in primary Pap-smear result. HPV was found in 143 (33%) specimens and the most comment high-risk and low-risk HPV types were HPV-16 and -6, respectively. Also, 62 (43%) were co-infected with multiple genotypes includes, 34 (24%) cases had co-infection with two HPV types, 17 (12%) cases had co-infection with three HPV types, 6 (4%) cases had co-infection with four HPV types and 5 (3%) cases had co-infection with five HPV types. There was statistically different domination on high-risk genotype in most of the co-infected samples (p<0.01).
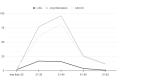
Conclusion: Current study indicates that the lesion pathology assessment was significantly associated with the HPV infection (p<0.01). Furthermore, the age group assessment shows that most of the HPV positive cases were 21 to 40 (p<0.01). The HPV infection prevalence in the current study was 33% and the most frequently reported high-risk and low-risk HPV types were 16 and 6, respectively.
Keywords: Co-infection; Human papillomavirus (HPV); In situ hybridization; Papillomavirus infections; Uterine cervical neoplasms.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of human papillomavirus genotypes in women with normal and abnormal cervical cytology in Iran.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006 Oct-Dec;7(4):529-32. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006. PMID: 17250423
-
Prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among women from quilombo communities in northeastern Brazil.BMC Womens Health. 2018 Jan 2;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12905-017-0499-3. BMC Womens Health. 2018. PMID: 29291721 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus genotype distribution and E6/E7 oncogene expression in Turkish women with cervical cytological findings.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(9):3997-4003. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.9.3997. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24935586
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) prevalence and types among women attending regular gynecological visit in Tehran, Iran.Clin Lab. 2014;60(2):267-73. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2013.130221. Clin Lab. 2014. PMID: 24660540
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, HIV infection and cervical cancer in Tanzania, east Africa.Int J Cancer. 1992 Jun 19;51(4):515-21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510403. Int J Cancer. 1992. PMID: 1318265
Cited by
-
Patterns of single and multiple HPV infections in female: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 18;10(17):e35736. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35736. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khorasanizadeh F, Hassanloo J, Khaksar N, Taheri SM, Marzaban M, Rashidi BH, et al. Epidemiology of cervical cancer and human papilloma virus infection among Iranian women—analyses of national data and systematic review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol 2013;128:277–281. - PubMed
-
- McCredie MR, Sharples KJ, Paul C, Baranyai J, Medley G, Jones RW, et al. Natural history of cervical neoplasia and risk of invasive cancer in women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 3: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol 2008;9:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Alam TM, Khan MM, Iqbal MA, Abdul W, Mushtaq M. Cervical cancer prediction through different screening methods using data mining. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 2019;10:388–396.
-
- Smith JS, Lindsay L, Hoots B, Keys J, Franceschi S, Winer R, et al. Human papillomavirus type distribution in invasive cervical cancer and high-grade cervical lesions: a meta-analysis update. Int J Cancer 2007;121:621–632. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials