Semaphorin 3G exacerbates joint inflammation through the accumulation and proliferation of macrophages in the synovium
- PMID: 35659346
- PMCID: PMC9166515
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02817-7
Semaphorin 3G exacerbates joint inflammation through the accumulation and proliferation of macrophages in the synovium
Abstract
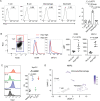
Objectives: Methotrexate (MTX) is an anchor drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the precise mechanisms by which MTX stalls RA progression and alleviates the ensuing disease effects remain unknown. The aim of the present study was to identify novel therapeutic target molecules, the expression patterns of which are affected by MTX in patients with RA.
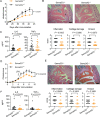
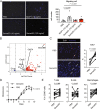
Methods: CD4+ T cells from 28 treatment-naïve patients with RA before and 3 months after the initiation of MTX treatment were subjected to DNA microarray analyses. The expression levels of semaphorin 3G, a differentially expressed gene, and its receptor, neuropilin-2, were evaluated in the RA synovium and collagen-induced arthritis synovium. Collagen-induced arthritis and collagen antibody-induced arthritis were induced in semaphorin3G-deficient mice and control mice, and the clinical score, histological score, and serum cytokines were assessed. The migration and proliferation of semaphorin 3G-stimulated bone marrow-derived macrophages were analyzed in vitro. The effect of local semaphorin 3G administration on the clinical score and number of infiltrating macrophages during collagen antibody-induced arthritis was evaluated.
Results: Semaphorin 3G expression in CD4+ T cells was downregulated by MTX treatment in RA patients. It was determined that semaphorin 3G is expressed in RA but not in the osteoarthritis synovium; its receptor neuropilin-2 is primarily expressed on activated macrophages. Semaphorin3G deficiency ameliorated collagen-induced arthritis and collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Semaphorin 3G stimulation enhanced the migration and proliferation of bone marrow-derived macrophages. Local administration of semaphorin 3G deteriorated collagen antibody-induced arthritis and increased the number of infiltrating macrophages.
Conclusions: Upregulation of semaphorin 3G in the RA synovium is a novel mechanism that exacerbates joint inflammation, leading to further deterioration, through macrophage accumulation.
Keywords: Macrophage; Methotrexate; Neuropilin-2; Rheumatoid arthritis; Semaphorin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble neuropilin-2, a nerve repellent receptor, is increased in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and aggravates sympathetic fiber repulsion and arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Oct;60(10):2892-901. doi: 10.1002/art.24860. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19790074
-
Sinomenine Inhibits the Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating the Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines and Monocyte/Macrophage Subsets.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 26;9:2228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02228. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319663 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine Mediated Biomimetic Delivery of Methotrexate by Albumin-Based Nanomedicines for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy.ACS Nano. 2019 May 28;13(5):5036-5048. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01710. Epub 2019 Apr 25. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 30978282
-
Regulatory role of KCa3.1 in immune cell function and its emerging association with rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:997621. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997621. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methotrexate: a gold standard for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2014 Dec;28(4):351-8. doi: 10.3109/15360288.2014.959238. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 25322199 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship of ALPK1, hyaluronic acid and M1 macrophage polarization in the temporomandibular joint synovitis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18172. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18172. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38494837 Free PMC article.
-
TAp63, a methotrexate target in CD4+ T cells, suppresses Foxp3 expression and exacerbates autoimmune arthritis.JCI Insight. 2023 May 22;8(10):e164778. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.164778. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37212280 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Semaphorins in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2024 Apr 2;13(7):618. doi: 10.3390/cells13070618. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bivalent chromatin accommodates survivin and BRG1/SWI complex to activate DNA damage response in CD4+ cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 11;22(1):440. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01814-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39261837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh JA, Cameron C, Noorbaloochi S, Cullis T, Tucker M, Christensen R, Ghogomu ET, Coyle D, Clifford T, Tugwell P, et al. Risk of serious infection in biological treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2015;386(9990):258–265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61704-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Yazici Y, Sokka T, Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Methotrexate as the "anchor drug" for the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21(5 Suppl 31):S179–S185. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, McInnes IB, Sepriano A, van Vollenhoven RF, de Wit M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685–699. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

