MicroRNA-96: A therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker
- PMID: 35656454
- PMCID: PMC9118275
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.59604.13226
MicroRNA-96: A therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker
Abstract
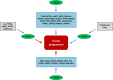
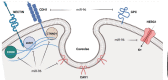
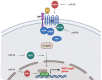
Cancer has been always considered as one of the main human health challenges worldwide. One of the main causes of cancer-related mortality is late diagnosis in the advanced stages of the disease, which reduces the therapeutic efficiency. Therefore, novel non-invasive diagnostic methods are required for the early detection of tumors and improving the quality of life and survival in cancer patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have pivotal roles in various cellular processes such as cell proliferation, motility, and neoplastic transformation. Since circulating miRNAs have high stability in body fluids, they can be suggested as efficient noninvasive tumor markers. MiR-96 belongs to the miR-183-96-182 cluster that regulates cell migration and tumor progression as an oncogene or tumor suppressor by targeting various genes in solid tumors. In the present review, we have summarized all of the studies that assessed the role of miR-96 during tumor progression. This review clarifies the molecular mechanisms and target genes recruited by miR-96 to regulate tumor progression and metastasis. It was observed that miR-96 mainly affects tumorigenesis by targeting the structural proteins and FOXO transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of the microRNA-132 during tumor progressions.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Aug 21;21(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02149-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34419060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-377: A therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 31;226:1226-1235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.236. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36442575 Review.
-
MicroRNA-217: a therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022 Jan;22(1):61-76. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2022.2017284. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 34883033 Review.
-
Role of microRNA-363 during tumor progression and invasion.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;80(3):481-499. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01022-1. Epub 2024 May 1. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38691273 Review.
-
Role of microRNA-494 in tumor progression.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6342-6361. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Selected miRNAs in Normal and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and in BxPc3 and MIA PaCa-2 Cell Lines of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3617. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043617. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835029 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Human Samples and Cell Lines Revealed Nine miRNAs Associated with Cisplatin Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 28;25(7):3793. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073793. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612604 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-495: a therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker.J Mol Histol. 2023 Dec;54(6):559-578. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10159-0. Epub 2023 Sep 28. J Mol Histol. 2023. PMID: 37759132 Review.
-
Aquaporin Expression and Regulation in Clinical and Experimental Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):487. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010487. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-183 cluster: a promising biomarker and therapeutic target in gastrointestinal malignancies.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;13(12):6147-6175. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38187051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen J, Zhang K, Xu Y, Gao Y, Li C, Wang R, et al. The role of microRNA-26a in human cancer progression and clinical application. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:7095–7108. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G. Circulating miRNAs: Roles in cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:75–93. - PubMed
-
- Cuk K, Zucknick M, Heil J, Madhavan D, Schott S, Turchinovich A, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:1602–1612. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
