Antiviral Effect of Polyphenolic Substances in Geranium wilfordii Maxim against HSV-2 Infection Using in vitro and in silico Approaches
- PMID: 35646147
- PMCID: PMC9132656
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7953728
Antiviral Effect of Polyphenolic Substances in Geranium wilfordii Maxim against HSV-2 Infection Using in vitro and in silico Approaches
Abstract
Background: Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) infestation was the most widespread STD (sexually transmitted diseases) among humans and was the leading cause of infectious recurrent genital herpes. Existing therapies against HSV-2 did incompletely restrain the comeback of activated HSV-2 infestation. Geranium wilfordii Maxim had long been used as traditional Chinese medicine for treating the diseases owing to its anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects. Herein, the study was designed to investigate the antiviral activity of G.wilfordii and its potential effect in regulating the host's immune response.
Methods: To identify the stage of infection at which the compounds inhibited HSV-2, we performed virucidal, therapeutic, and prophylactic assays. The antiviral efficacy was evaluated by the analysis of viral components HSV-2 gD and VP16. The antiviral activities of these compounds were also evaluated by phenotypic analysis, such as cell proliferation and apoptosis. Molecular docking studies on candidate compounds were done to indicate binding interactions between the compounds and adopted compound targets.
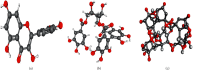
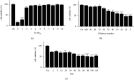
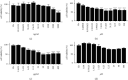
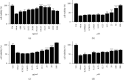
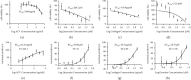
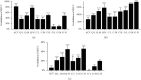
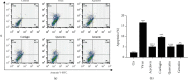
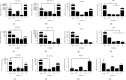
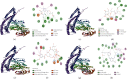
Results: Quercetin, corilagin, and geraniin inhibited the replication of HSV-2, with geraniin showing greater TI. The obtained IC50 value of quercetin was 204.7 μM and TI (IC50/EC50) was 5.1, whereas the obtained IC50 value of corilagin was 118.0 μg/ml and TI was 4.05. Geraniin exhibited prominent antiviral activity with an IC50 of 212.4 μM and an EC50 of 18.37 μM, resulting in a therapeutic index (TI) of 11.56. Geraniin showed important in vitro virucidal activity through blocking viral attachment. Compared with the virus group, the apoptosis rates in quercetin-, corilagin-, and geraniin-treated groups were significantly decreased (p < 0.001).The expressions at the transcription genes of virus own replication key factors (including HSV-2 gD and VP16) and cytokines (including TBK1) of infected cells treated with quercetin, corilagin, and geraniin were inhibited. The in silico approaches demonstrated a high number of potential strong intermolecular interactions as hydrogen bonds between geraniin, corilagin, and the activity site of HSV-2 gD. Molecular docking studies demonstrated the effects of corilagin by targeting TBK1.
Conclusions: Together, these results highlighted the importance of G.wilfordii treatment in HSV-2 infection and underscored its therapeutic potential. However, additional in vitro and in vivo research was required to validate our findings.
Copyright © 2022 Hao Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
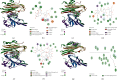

Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Systematic Analysis of Molecular Mechanisms of Geranium wilfordii Maxim for HSV-2 Infection.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 3;2021:1009551. doi: 10.1155/2021/1009551. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34777530 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Potential of Spondias mombin L. Leaves Extract Against Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Replication Using In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Planta Med. 2020 May;86(7):505-515. doi: 10.1055/a-1135-9066. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Planta Med. 2020. PMID: 32247285
-
In vitro and silico studies of geraniin interfering with HSV-2 replication by targeting glycoprotein D.Nat Prod Res. 2024 Jun;38(12):2053-2059. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2023.2241153. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Nat Prod Res. 2024. PMID: 37585693
-
Geranium wilfordii maxim.: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and toxicology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114907. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114907. Epub 2021 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34896206 Review.
-
[Development of antiviral therapeutic agents from traditional medicines].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998 Sep;118(9):383-400. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.118.9_383. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9778999 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and the Management of Herpes Labialis.Viruses. 2023 Jan 13;15(1):225. doi: 10.3390/v15010225. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

