Brain Gray Matter Atrophy and Functional Connectivity Remodeling in Patients With Chronic LHON
- PMID: 35645726
- PMCID: PMC9135140
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.885770
Brain Gray Matter Atrophy and Functional Connectivity Remodeling in Patients With Chronic LHON
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the brain gray matter volume (GMV) and spontaneous functional connectivity (FC) changes in patients with chronic Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), and their relations with clinical measures.
Methods: A total of 32 patients with chronic LHON and matched sighted healthy controls (HC) underwent neuro-ophthalmologic examinations and multimodel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) was used to detect the GMV differences between the LHON and HC. Furthermore, resting-state FC analysis using the VBM-identified clusters as seeds was carried out to detect potential functional reorganization in the LHON. Finally, the associations between the neuroimaging and clinical measures were performed.
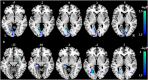
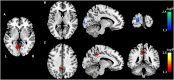
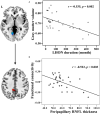
Results: The average peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness of the chronic LHON was significantly thinner (T = -16.421, p < 0.001), and the mean defect of the visual field was significantly higher (T = 11.28, p < 0.001) than the HC. VBM analysis demonstrated a significantly lower GMV of bilateral calcarine gyri (CGs) in the LHON than in the HC (p < 0.05). Moreover, in comparison with the HC, the LHON had significantly lower FC between the centroid of the identified left CG and ipsilateral superior occipital gyrus (SOG) and higher FC between this cluster and the ipsilateral posterior cingulate gyrus (p < 0.05, corrected). Finally, the GMV of the left CG was negatively correlated with the LHON duration (r = -0.535, p = 0.002), and the FC between the left CG and the ipsilateral posterior cingulate gyrus of the LHON was negatively correlated with the average peripapillary RNFL thickness (r = -0.522, p = 0.003).
Conclusion: The atrophied primary visual cortex of the chronic LHON may be caused by transneuronal degeneration following the retinal damage. Moreover, our findings suggest that the functional organization of the atrophied primary visual cortex has been reshaped in the chronic LHON.
Keywords: LHON; functional connectivity (FC); gray matter volume (GMV); reorganization; visual cortex (V1).
Copyright © 2022 Tian, Wang, Zhang, Fan, Liang, Shi, Qin and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence for retrochiasmatic tissue loss in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Hum Brain Mapp. 2010 Dec;31(12):1900-6. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20985. Epub 2010 May 13. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010. PMID: 20827728 Free PMC article.
-
Brain white matter changes in asymptomatic carriers of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.J Neurol. 2019 Jun;266(6):1474-1480. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09284-2. Epub 2019 Mar 25. J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30911824
-
Abnormal large-scale structural rich club organization in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Neuroimage Clin. 2021;30:102619. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102619. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Neuroimage Clin. 2021. PMID: 33752075 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths With Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;73(1):64-72. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2423. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26650724 Review.
-
Large-scale network abnormality in bipolar disorder: A multimodal meta-analysis of resting-state functional and structural magnetic resonance imaging studies.J Affect Disord. 2021 Sep 1;292:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.052. Epub 2021 May 27. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 34087634 Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant neurovascular coupling in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: Evidence from a multi-model MRI analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 10;16:1050772. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1050772. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36703998 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal cerebral blood flow in patients with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Brain Imaging Behav. 2023 Oct;17(5):471-480. doi: 10.1007/s11682-023-00775-5. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. PMID: 37368154
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

