Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction improves inflammatory response and metabolic bone disorder in inflammatory bowel disease-induced bone loss
- PMID: 35645540
- PMCID: PMC9099185
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i13.1315
Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction improves inflammatory response and metabolic bone disorder in inflammatory bowel disease-induced bone loss
Abstract
Background: Bone loss and osteoporosis are commonly described as extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction (JQBD) is a prescription used in clinical practice. However, further studies are needed to determine whether JQBD regulates the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) (RANK)/receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)/ osteoprotegerin (OPG) pathways and could play a role in treating IBD-induced bone loss.
Aim: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of JQBD in IBD-induced bone loss and explore the underlying mechanisms.
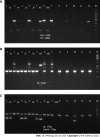
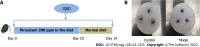
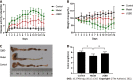
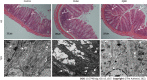
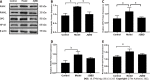
Methods: An IBD-induced bone loss model was constructed by feeding 12 6-to-8-wk-old interleukin-10 (IL-10)-knockout mice with piroxicam for 10 d. The mice were randomly divided into model and JQBD groups. We used wild-type mice as a control. The JQBD group was administered the JQBD suspension for 2 wk by gavage, while the control and model groups were given normal saline at the corresponding time points. All mice were killed after the intervention. The effect of JQBD on body weight, disease activity index (DAI), and colon length was analyzed. Histopathological examination, colon ultrastructure observation, and micro-computed tomographic scanning of the lumbar vertebrae were performed. The gene expression of NF-κB, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 in the colon was evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Colon samples were assessed by Western blot for the expression of RANKL, OPG, RANK, and NF-κB proteins.
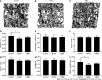
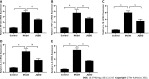
Results: The model group lost body weight, had a shorter colon, and showed a dramatic increase in DAI score, whereas JQBD had protective and therapeutic effects. Treatment with JQBD significantly improved inflammatory cell infiltration and reduced crypt abscess and ulcer formation. Three-dimensional imaging of the vertebral centrum in the model group revealed a lower bone mass, loose trabeculae, and "rod-shaped" changes in the structure compared to the control group and JQBD groups. The bone volume/total volume ratio and bone mineral density were significantly lower in the model group than in the control group. JQBD intervention downregulated the NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 mRNA expression levels. The RANKL and OPG protein levels were also improved.
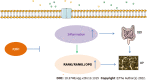
Conclusion: JQBD reduces inflammation of the colonic mucosa and inhibits activation of the RANK/ RANKL/OPG signaling pathway, thereby reducing osteoclast activation and bone resorption and improving bone metabolism.
Keywords: Bone metabolism; Inflammation; Inflammatory bowel disease; Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction; Osteoporosis.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jianpi Qingchang decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 21;23(7):1180-1188. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1180. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28275298 Free PMC article.
-
Jianpi Qingchang Decoction Ameliorates Chronic Colitis in Piroxicam-Induced IL-10 Knockout Mice by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Feb 9;2022:7378807. doi: 10.1155/2022/7378807. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35186102 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of Zhenwu Decoction in improving renal inflammatory injury in mice with DN of spleen-kidney Yang deficiency syndrome by regulating ROCK/IKK/NF-κB pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Sep;48(18):5041-5048. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230512.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802846 Chinese.
-
Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Bone. 2002 Feb;30(2):340-6. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00682-2. Bone. 2002. PMID: 11856640 Review.
-
Role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin in bone cell biology.J Mol Med (Berl). 2001 Jun;79(5-6):243-53. doi: 10.1007/s001090100226. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11485016 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics Analysis to Identify Key Immune Genes for Osteoporosis based on Machine Learning and Single-cell Analysis.Orthop Surg. 2024 Nov;16(11):2803-2820. doi: 10.1111/os.14172. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 39238187 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of action and synergetic formulas of plant-based natural compounds from traditional Chinese medicine for managing osteoporosis: a literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 28;10:1235081. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1235081. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37700771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant traditional Chinese Medicine in treatment and prevention of osteoporosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 27;14:1203767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1203767. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37441527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mitophagy in metabolic diseases and its exercise intervention.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1339128. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1339128. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38348222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic analysis and validation of diagnostic marker genes in patients with osteoporosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:987937. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.987937. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olpin JD, Sjoberg BP, Stilwill SE, Jensen LE, Rezvani M, Shaaban AM. Beyond the Bowel: Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Radiographics. 2017;37:1135–1160. - PubMed
-
- Shao BZ, Wang SL, Pan P, Yao J, Wu K, Li ZS, Bai Y, Linghu EQ. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Putting out the Fire of Inflammation. Inflammation. 2019;42:1147–1159. - PubMed
-
- Sairenji T, Collins KL, Evans DV. An Update on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Prim Care. 2017;44:673–692. - PubMed
-
- Malik TA. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Historical Perspective, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors. Surg Clin North Am. 2015;95:1105–1122, v. - PubMed
-
- Greuter T, Vavricka SR. Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease - epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13:307–317. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

