Unveiling the Multitarget Anti-Alzheimer Drug Discovery Landscape: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 35631371
- PMCID: PMC9146451
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15050545
Unveiling the Multitarget Anti-Alzheimer Drug Discovery Landscape: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
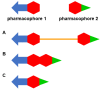
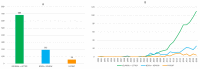
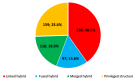
Multitarget anti-Alzheimer agents are the focus of very intensive research. Through a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the publications in the period 1990-2020, we have identified trends and potential gaps that might guide future directions. We found that: (i) the number of publications boomed by 2011 and continued ascending in 2020; (ii) the linked-pharmacophore strategy was preferred over design approaches based on fusing or merging pharmacophores or privileged structures; (iii) a significant number of in vivo studies, mainly using the scopolamine-induced amnesia mouse model, have been performed, especially since 2017; (iv) China, Italy and Spain are the countries with the largest total number of publications on this topic, whereas Portugal, Spain and Italy are the countries in whose scientific communities this topic has generated greatest interest; (v) acetylcholinesterase, β-amyloid aggregation, oxidative stress, butyrylcholinesterase, and biometal chelation and the binary combinations thereof have been the most commonly pursued, while combinations based on other key targets, such as tau aggregation, glycogen synthase kinase-3β, NMDA receptors, and more than 70 other targets have been only marginally considered. These results might allow us to spot new design opportunities based on innovative target combinations to expand and diversify the repertoire of multitarget drug candidates and increase the likelihood of finding effective therapies for this devastating disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; animal models; hybrids; multifactorial diseases; multitarget drug design; multitarget drugs; polypharmacology; target combinations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stepwise Structural Simplification of the Dihydroxyanthraquinone Moiety of a Multitarget Rhein-Based Anti-Alzheimer Lead to Improve Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Properties.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 25;16(8):982. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16080982. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204327 Free PMC article.
-
Management of oxidative stress and other pathologies in Alzheimer's disease.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Sep;93(9):2491-2513. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02538-y. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31440798 Review.
-
Molecular hybridization: a powerful tool for multitarget drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024 Apr;19(4):451-470. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2322990. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38456452 Review.
-
Dual GSK-3β/AChE Inhibitors as a New Strategy for Multitargeting Anti-Alzheimer's Disease Drug Discovery.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018 Feb 9;9(3):171-176. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00463. eCollection 2018 Mar 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29541355 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors as potential anti-Alzheimer's agents: an updated patent review (2018-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022 Aug;32(8):913-932. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2022.2083956. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022. PMID: 35623095
Cited by
-
A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of Exercise Intervention Publications for Alzheimer's Disease (1998-2021).J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 6;11(19):5903. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195903. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233770 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise Structural Simplification of the Dihydroxyanthraquinone Moiety of a Multitarget Rhein-Based Anti-Alzheimer Lead to Improve Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Properties.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 25;16(8):982. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16080982. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204327 Free PMC article.
-
A Combined Chronic Low-Dose Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Acetylcholinesterase Pharmacological Inhibition Promotes Memory Reinstatement in Alzheimer's Disease Mice Models.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;15(8):908. doi: 10.3390/ph15080908. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893732 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-Class Selenium-Containing Potent Serotonin Receptor 5-HT6 Agents with a Beneficial Neuroprotective Profile against Alzheimer's Disease.J Med Chem. 2024 Jan 25;67(2):1580-1610. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02148. Epub 2024 Jan 8. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38190615 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Metal Cations of Copper, Iron, and Aluminum and Multifunctional Ligands in Alzheimer's Disease: Experimental and Computational Insights.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 25;8(5):4508-4526. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06939. eCollection 2023 Feb 7. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36777601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International . World Alzheimer Report 2019: Attitudes to Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2019.
-
- World Health Organization The Top 10 Causes of Death. [(accessed on 5 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- ClinicalTrials.gov A Study of Sodium Oligomannate (GV-971) in Participants with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (GREEN MEMORY) [(accessed on 5 January 2022)]; Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04520412.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

