Impact of Group II Baculovirus IAPs on Virus-Induced Apoptosis in Insect Cells
- PMID: 35627135
- PMCID: PMC9140827
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13050750
Impact of Group II Baculovirus IAPs on Virus-Induced Apoptosis in Insect Cells
Abstract
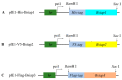
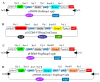
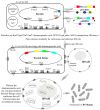
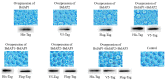
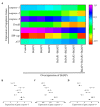
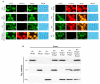
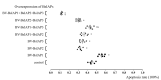
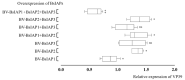
Apoptosis plays an important role in virus-host interactions and is a major element of the insect immune response. Exploring the regulatory mechanisms of virus-induced apoptosis through the expression of apoptotic genes holds important research and application value. Functional research on the reported inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) mainly focuses on the group I baculovirus, while the functions of the group II baculovirus IAPs remains unclear. To explore its role in the regulation of the apoptosis of insect cells, we constructed the transient expression vector (pIE1 vectors) and the recombinant baculovirus expressing Bsiap genes (from the Buzura suppressaria nucleopolyhedrovirus) of the group II baculovirus. Apoptosis gene expression results and the virus-induced apoptosis rate show that the overexpression of BsIAP1 could promote apoptosis in insect cells. However, the overexpression of BsIAP2 and BsIAP3 decreases the expression of apoptotic genes, revealing an inhibitory effect. Results on the impact of baculovirus-induced apoptosis also confirm that BsIAP1 reduces viral nucleocapsid expression and the baculovirus titer, while BsIAP2 and BsIAP3 increase them significantly. Furthermore, compared with single expression, the co-expression of BsIAP2 and BsIAP3 significantly reduces the rate of virus-induced apoptosis and improves the expression of nucleocapsids and the titer of offspring virus, indicating the synergistic effect on BsIAP2 and BsIAP3. In addition, combined expression of all three BsIAPs significantly reduced levels of intracellular apoptosis-related genes (including apoptosis and anti-apoptosis genes), as well as apoptosis rate and progeny virus titer, indicating that life activities in insect cells are also inhibited. These findings reveal the relationship between apoptosis and group II baculovirus IAP, which provide an experimental and theoretical basis for further exploration of the molecular mechanism between group II baculoviruses and insect cells.
Keywords: apoptosis; group II baculovirus; inhibitor of apoptosis protein; insect cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evolutionary and functional analyses of the interaction between the Bombyx mori inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) and nucleopolyhedrovirus IAPs.Insect Sci. 2020 Jun;27(3):463-474. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12664. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Insect Sci. 2020. PMID: 30697933
-
Host insect inhibitor-of-apoptosis SfIAP functionally replaces baculovirus IAP but is differentially regulated by Its N-terminal leader.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):11448-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01311-10. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20739517 Free PMC article.
-
Insect inhibitor-of-apoptosis (IAP) proteins are negatively regulated by signal-induced N-terminal degrons absent within viral IAP proteins.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4481-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03659-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653450 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in insect-baculovirus interactions.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Dec;127:103459. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2020.103459. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32961323 Review.
-
Baculovirus--insect cell interactions.Cytotechnology. 1996;20(1-3):73-93. doi: 10.1007/BF00350390. Cytotechnology. 1996. PMID: 8987578 Review.
Cited by
-
SMAC Mimetics for the Treatment of Lung Carcinoma: Present Development and Future Prospects.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1334-1352. doi: 10.2174/0113895575269644231120104501. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38275029 Review.
-
Impact of the Transboundary Interference Inhibitor on RNAi and the Baculovirus Expression System in Insect Cells.Insects. 2024 May 21;15(6):375. doi: 10.3390/insects15060375. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38921090 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis or Antiapoptosis? Interrupted Regulated Cell Death of Host Cells by Ascovirus Infection In Vitro.mBio. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):e0311922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03119-22. Epub 2023 Feb 6. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36744941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu H., Wang J., Gao H., Li S., Zhang Y., Zheng N. Heat-induced apoptosis and gene expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016;56:918. doi: 10.1071/AN14420. - DOI
-
- Xu H.L., Yu X.F., Qu S.C., Zhang R., Qu X.R., Chen Y.P., Ma X.Y., Sui D.Y. Anti-proliferative effect of Juglone from Juglans mandshurica Maxim on human leukemia cell HL-60 by inducing apoptosis through the mitochondria-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010;645:14–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.06.072. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

