The effect of apigenin and chemotherapy combination treatments on apoptosis-related genes and proteins in acute leukaemia cell lines
- PMID: 35614109
- PMCID: PMC9132959
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11441-z
The effect of apigenin and chemotherapy combination treatments on apoptosis-related genes and proteins in acute leukaemia cell lines
Abstract
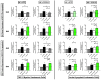
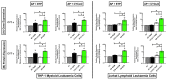
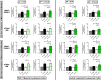
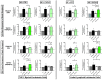
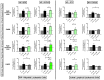
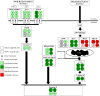
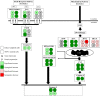
Apigenin is a dietary polyphenol found abundantly in fruit and vegetables, which sensitizes leukaemia cells to topoisomerase inhibitor agents (e.g., etoposide), and alkylating agents (e.g., cyclophosphamide), reducing ATP levels and inducing apoptosis; whilst being protective to control haematopoietic stem cells. This study analysed the expression profiles of intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis-related genes and proteins to help elucidate the mechanisms of action of apigenin when used in combination with etoposide or cyclophosphamide in lymphoid and myeloid leukaemia cell lines (Jurkat and THP-1). Expression of apoptosis-related genes were measured using a TaqMan® Human Apoptosis Array and the StepOne Plus RT-qPCR System, whilst apoptosis-related proteins were determined using a protein profiler™-human apoptosis array and the LI-COR OdysseyR Infrared Imaging System. Apigenin when combined with etoposide or cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway, increasing the expression of pro-apoptotic cytochrome c, SMAC/DIABLO, and HTRA2/OMI, which promoted caspase-9 and -3 activation. Targeting anti-apoptotic and/or pro-apoptotic members of the apoptotic pathways is a promising strategy to induce cancer cell death and improve sensitivity to chemotherapy agents. Here the apoptotic pathways induced by apigenin in combination with etoposide or cyclophosphamide were identified within human leukaemia cell lines, such applications could provide combination therapies for the treatment of leukaemia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Endogenously released Smac is insufficient to mediate cell death of human lung carcinoma in response to etoposide.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Aug 1;298(1):83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.007. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15242764
-
A small molecule Smac-mimic compound induces apoptosis and sensitizes TRAIL- and etoposide-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2005 Nov 10;24(49):7381-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208888. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16044155
-
Novel second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac) mimetic compounds sensitize human leukemic cell lines to conventional chemotherapeutic drug-induced and death receptor-mediated apoptosis.Invest New Drugs. 2011 Dec;29(6):1264-75. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9475-6. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Invest New Drugs. 2011. PMID: 20614162
-
Polyphenols enhance the activity of alkylating agents in leukaemia cell lines.Oncotarget. 2019 Jul 16;10(44):4570-4586. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27068. eCollection 2019 Jul 16. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31360305 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin role as cell-signaling pathways modulator: implications in cancer prevention and treatment.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Apr 1;21(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01888-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33794890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Apigenin in Cancer Prevention and Treatment.Molecules. 2022 Sep 16;27(18):6051. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186051. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Polymeric Colloids for Cancer Treatment.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;14(24):5445. doi: 10.3390/polym14245445. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apigenin: A Bioflavonoid with a Promising Role in Disease Prevention and Treatment.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 18;12(6):1353. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061353. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Involvement of Natural Polyphenols in Molecular Mechanisms Inducing Apoptosis in Tumor Cells: A Promising Adjuvant in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1680. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021680. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensive review on breast cancer its etiology, progression, prognostic markers, and treatment.Med Oncol. 2023 Jul 14;40(8):238. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02111-9. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37442848 Review.
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available at https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers. Accessed 01 June 2021.
-
- Hassanpour SH, Dehghani MA, Karami SZ, Dehghani F. Role of apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of leukemia types. Ann. Blood Cancer. 2018;1:1002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

