NURR1-deficient mice have age- and sex-specific behavioral phenotypes
- PMID: 35593070
- PMCID: PMC9539971
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.25067
NURR1-deficient mice have age- and sex-specific behavioral phenotypes
Abstract
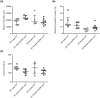
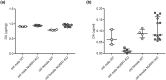
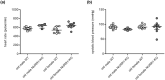
The transcription factor NURR1 is essential to the generation and maintenance of midbrain dopaminergic (mDA) neurons and its deregulation is involved in the development of dopamine (DA)-associated brain disorders, such as Parkinson's disease (PD). The old male NURR1 heterozygous knockout (NURR1-KO) mouse has been proposed as a model of PD due to its altered motor performance that was, however, not confirmed in a subsequent study. Based on these controversial results, we explored the effects of the NURR1 deficiency on locomotor activity, motor coordination, brain and plasma DA levels, blood pressure and heart rate of old mice, also focusing on the potential effect of sex. As a probable consequence of the role of NURR1 in DA pathway, we observed that the old NURR1-KO mouse is characterized by motor impairment, and increased brain DA level and heart rate, independently from sex. However, we also observed an alteration in spontaneous locomotor activity that only affects males. In conclusion, NURR1 deficiency triggers sex- and age-specific alterations of behavioral responses, of DA levels and cardiovascular abnormalities. Further studies in simplified systems will be necessary to dissect the mechanism underlying these observations.
Keywords: NURR1; Parkinson's disease; dopamine; locomotion; motor impairment; murine model.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Neuroscience Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NURR1 deficiency is associated to ADHD-like phenotypes in mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 27;9(1):207. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0544-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31455763 Free PMC article.
-
Nurr1 deficiency shortens free running period, enhances photoentrainment to phase advance, and disrupts circadian cycling of the dopamine neuron phenotype.Behav Brain Res. 2021 Aug 6;411:113347. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113347. Epub 2021 May 13. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33991560
-
NURR1 in Parkinson disease--from pathogenesis to therapeutic potential.Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Nov;9(11):629-36. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.209. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24126627 Review.
-
Elevated locomotor activity without altered striatal dopamine contents in Nurr1 heterozygous mice after acute exposure to methamphetamine.Behav Brain Res. 2003 Jul 14;143(1):95-100. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(03)00029-9. Behav Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12842300
-
The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.001. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16243425 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain nuclear receptors and cardiovascular function.Cell Biosci. 2023 Jan 20;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-00962-3. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36670468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-dimorphic neuroprotective effect of CD163 in an α-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Dec 13;9(1):164. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00606-w. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 38092806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buervenich, S. , Carmine, A. , Arvidsson, M. , Xiang, F. , Zhang, Z. , Sydow, O. , Jönsson, E. G. , Sedvall, G. C. , Leonard, S. , Ross, R. G. , Freedman, R. , Chowdari, K. V. , Nimgaonkar, V. L. , Perlmann, T. , Anvret, M. , & Olson, L. (2000). NURR1 mutations in cases of schizophrenia and manic‐depressive disorder, 813(February), 808–813. - PubMed
-
- De Miranda, B. R. , Popichak, K. A. , Hammond, S. L. , Jorgensen, B. A. , Aaron, T. , Safe, S. , & Tjalkens, R. B. (2015). The Nurr1 activator 1,1‐bis(3′‐indolyl)‐1‐(p‐chlorophenyl)methane blocks inflammatory gene expression in BV‐2 microglial cells by inhibiting NF‐κB. Molecular Pharmacology, 87(6), 1021–1034. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

