A novel strategy for optimal component formula of anti-PRRSV from natural compounds using tandem mass tag labeled proteomic analyses
- PMID: 35568854
- PMCID: PMC9106989
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-022-03184-w
A novel strategy for optimal component formula of anti-PRRSV from natural compounds using tandem mass tag labeled proteomic analyses
Abstract
Background: Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS) is one of the most important porcine viral diseases which have been threatening the pig industry in China. At present, most commercial vaccines fail to provide complete protection because of highly genetic diversity of PRRSV strains. This study aimed to optimize a component formula from traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)compounds with defined chemical characteristics and clear mechanism of action against PRRSV.
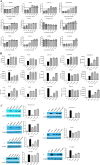
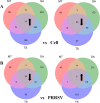
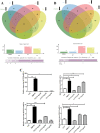
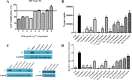
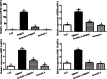
Methods: A total of 13 natural compounds were screened for the anti-PRRSV activity using porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs). Three compounds with strong anti-PRRSV activity were selected to identify their potential protein targets by proteomic analysis. The optimal compound formula was determined by orthogonal design based on the results of proteomics. MTT assay was used to determine the maximum non-cytotoxic concentration (MNTC) of each compound using PAMs. QPCR and western blot were used to investigate the PRRSV N gene and protein expression, respectively. The Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) technique of relative quantitative proteomics was used to detect the differential protein expression of PAMs treated with PRRSV, matrine (MT), glycyrrhizic acid (GA) and tea saponin (TS), respectively. The three concentrations of these compounds with anti-PRRSV activity were used for orthogonal design. Four formulas with high safety were screened by MTT assay and their anti-PRRSV effects were evaluated.
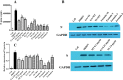
Results: MT, GA and TS inhibited PRRSV replication in a dose-dependent manner. CCL8, IFIT3, IFIH1 and ISG15 were the top four proteins in expression level change in cells treated with MT, GA or TS. The relative expression of IFIT3, IFIH1, ISG15 and IFN-β mRNAs were consistent with the results of proteomics. The component formula (0.4 mg/mL MT + 0.25 mg/mL GA + 1.95 μg/mL TS) showed synergistic anti-PRRSV effect.
Conclusions: The component formula possessed anti-PRRSV activity in vitro, in which the optimal dosage on PAMs was 0.4 mg/mL MT + 0.25 mg/mL GA + 1.95 μg/mL TS. Compatibility of the formula was superposition of the same target with GA and TS, while different targets of MT. IFN-β may be one of the targets of the component formula possessed anti-PRRSV activity.
Keywords: Glycyrrhizic acid; IFN-β; Matrine; PRRSV; TMT; Tea saponin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest in the research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon inducible porcine 2', 5'-oligoadenylate synthetase like-1 protein limits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 infection via the MDA5-mediated interferon-signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Oct;111:109151. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109151. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36007390
-
In vitro evaluation of antiviral activity of tea seed saponins against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Antivir Ther. 2015;20(7):743-52. doi: 10.3851/IMP2937. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Antivir Ther. 2015. PMID: 25609356
-
Identification of the RNA Pseudoknot within the 3' End of the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Genome as a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern To Activate Antiviral Signaling via RIG-I and Toll-Like Receptor 3.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e00097-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00097-18. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29618647 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of matrine and glycyrrhizic acid on porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Vitro and in vivo.Virol J. 2024 Jul 4;21(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02415-w. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38965549 Free PMC article.
-
From fuzziness to precision medicine: on the rapidly evolving proteomics with implications in mitochondrial connectivity to rare human disease.iScience. 2021 Jan 6;24(2):102030. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.102030. eCollection 2021 Feb 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33521598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to reveal the target of matrine against PRRSV.iScience. 2023 Mar 10;26(4):106371. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106371. eCollection 2023 Apr 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37009229 Free PMC article.
-
Target Discovery of Matrine against PRRSV in Marc-145 Cells via Activity-Based Protein Profiling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 16;24(14):11526. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411526. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511286 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans.Molecules. 2023 Apr 21;28(8):3628. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083628. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao D, Yang B, Yuan X, Shen C, Zhang D, Shi X, Zhang T, Cui H, Yang J, Chen X, Hao Y, Zheng H, Zhang K, Liu X. Advanced research in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus co-infection with other pathogens in swine. Front Vet Sci. 2021;8:699561. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.699561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Renken C, Nathues C, Swam H, Fiebig K, Weiss C, Eddicks M, Rizmann M, Nathues H. Application of an economic calculator to determine the cost of porcine re-productive and respiratory syndrome at farm-level in 21 pig herds in Germany. Porcine Health Manag. 2021;7:3. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00183-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Song SJ, Zhao J, Leng CL, Fu J, Li C, Tang YD, Xiang LR, Peng JM, Wang Q, Zhao HY, An TQ, Cai XH, Zhang HL, Tian ZJ. A potential endemic strain in China: NADC34-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020;67:1730–1738. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13508. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

