Nucleolin Overexpression Predicts Patient Prognosis While Providing a Framework for Targeted Therapeutic Intervention in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35565346
- PMCID: PMC9101044
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092217
Nucleolin Overexpression Predicts Patient Prognosis While Providing a Framework for Targeted Therapeutic Intervention in Lung Cancer
Abstract
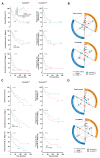
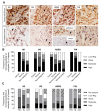
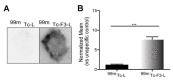
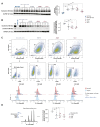
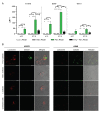
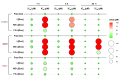
Notwithstanding the advances in the treatment of lung cancer with immune checkpoint inhibitors, the high percentage of non-responders supports the development of novel anticancer treatments. Herein, the expression of the onco-target nucleolin in patient-derived pulmonary carcinomas was characterized, along with the assessment of its potential as a therapeutic target. The clinical prognostic value of nucleolin for human pulmonary carcinomas was evaluated through data mining from the Cancer Genome Atlas project and immunohistochemical detection in human samples. Cell surface expression of nucleolin was evaluated by flow cytometry and subcellular fraction Western blotting in lung cancer cell lines. Nucleolin mRNA overexpression correlated with poor overall survival of lung adenocarcinoma cancer patients and further predicted the disease progression of both lung adenocarcinoma and squamous carcinoma. Furthermore, a third of the cases presented extra-nuclear expression, contrasting with the nucleolar pattern in non-malignant tissues. A two- to twelve-fold improvement in cytotoxicity, subsequent to internalization into the lung cancer cell lines of doxorubicin-loaded liposomes functionalized by the nucleolin-binding F3 peptide, was correlated with the nucleolin cell surface levels and the corresponding extent of cell binding. Overall, the results suggested nucleolin overexpression as a poor prognosis predictor and thus a target for therapeutic intervention in lung cancer.
Keywords: lung cancer; nucleolin expression; targeted intracellular drug delivery; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
V.M. was an employee and shareholder of TREAT U, SA. N.A.F. and A.C.G. were former employees at TREAT U, SA. S.S. and J.N.M. are shareholders of TREAT U, SA. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modelling the impact of nucleolin expression level on the activity of F3 peptide-targeted pH-sensitive pegylated liposomes containing doxorubicin.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Mar;12(3):629-646. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00972-z. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 33860446
-
Nucleolin overexpression in breast cancer cell sub-populations with different stem-like phenotype enables targeted intracellular delivery of synergistic drug combination.Biomaterials. 2015 Nov;69:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26283155
-
The Enhanced Efficacy of Intracellular Delivery of Doxorubicin/C6-Ceramide Combination Mediated by the F3 Peptide/Nucleolin System Is Supported by the Downregulation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 18;13(12):3052. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123052. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207464 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin is expressed in patient-derived samples and glioblastoma cells, enabling improved intracellular drug delivery and cytotoxicity.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Sep 1;370(1):68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.06.005. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29902537
-
Nucleolin; A tumor associated antigen as a potential lung cancer biomarker.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Dec;240:154160. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154160. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36335647 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolin‑based targeting strategies in cancer treatment: Focus on cancer immunotherapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Sep;52(3):81. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5284. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37477132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond biomarkers: Exploring the diverse potential of a novel phosphoprotein in lung cancer management.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Sep;28(18):e70077. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70077. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39304978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Travis W.D., Brambilla E., Nicholson A.G., Yatabe Y., Austin J.H.M., Beasley M.B., Chirieac L.R., Dacic S., Duhig E., Flieder D.B., et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015;10:1243–1260. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Planchard D., Popat S., Kerr K., Novello S., Smit E.F., Faivre-Finn C., Mok T.S., Reck M., Van Schil P.E., Hellmann M.D., et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:iv192–iv237. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- MultiNanoMed (Ref. 23240/IN0561)/European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
- Cancel Stem (reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016390)/European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
- CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-000012 (HealthyAging2020)/European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
- Euronanomed 2 (FCT reference ENMed/0005/2015)/European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
- MultiNanoMed (Ref. 23240/IN0561)/COMPETE 2020 - Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation
- Cancel Stem (reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016390)/COMPETE 2020 - Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation
- CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-000012 (HealthyAging2020)/COMPETE 2020 - Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation
- Euronanomed 2 (FCT reference ENMed/0005/2015)/COMPETE 2020 - Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation
- MultiNanoMed (Ref. 23240/IN0561)/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
- Cancel Stem (reference POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016390)/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
- CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-000012 (HealthyAging2020)/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
- Euronanomed 2 (FCT reference ENMed/0005/2015)/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
- CIBB (FCT references UIDB/04539/2020, UIDP/04539/2020 and LA/P/0058/2020)/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
- CIBB (FCT references UIDB/04539/2020, UIDP/04539/2020 and LA/P/0058/2020)/European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
- CIBB (FCT references UIDB/04539/2020, UIDP/04539/2020 and LA/P/0058/2020)/COMPETE 2020 - Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation
- SFRH/BD/51191/2010/FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

