Multifaceted and Intricate Oncogenic Mechanisms of NDRG1 in Head and Neck Cancer Depend on Its C-Terminal 3R-Motif
- PMID: 35563887
- PMCID: PMC9104279
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091581
Multifaceted and Intricate Oncogenic Mechanisms of NDRG1 in Head and Neck Cancer Depend on Its C-Terminal 3R-Motif
Abstract
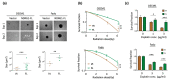
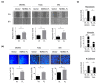
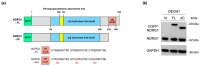
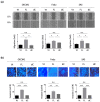
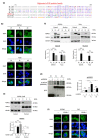
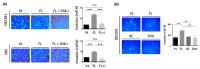
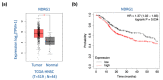
N-Myc downstream-regulated 1 (NDRG1) has inconsistent oncogenic functions in various cancers. We surveyed and characterized the role of NDRG1 in head and neck cancer (HNC). Cellular methods included spheroid cell formation, clonogenic survival, cell viability, and Matrigel invasion assays. Molecular techniques included transcriptomic profiling, RT-qPCR, immunoblotting, in vitro phosphorylation, immunofluorescent staining, and confocal microscopy. Prognostic significance was assessed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. NDRG1 participated in diverse oncogenic functions in HNC cells, mainly stress response and cell motility. Notably, NDRG1 contributed to spheroid cell growth, radio-chemoresistance, and upregulation of stemness-related markers (CD44 and Twist1). NDRG1 facilitated cell migration and invasion, and was associated with modulation of the extracellular matrix molecules (fibronectin, vimentin). Characterizing the 3R-motif in NDRG1 revealed its mechanism in the differential regulation of the phenotypes. The 3R-motif displayed minimal effect on cancer stemness but was crucial for cell motility. Phosphorylating the motif by GSK3b at serine residues led to its nuclear translocation to promote motility. Clinical analyses supported the oncogenic function of NDRG1, which was overexpressed in HNC and associated with poor prognosis. The data elucidate the multifaceted and intricate mechanisms of NDRG1 in HNC. NDRG1 may be a prognostic indicator or therapeutic target for refractory HNC.
Keywords: 3R-motif; NDRG1; cancer stemness; cell motility; head and neck cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 downregulates cell proliferation, invasiveness, and tumorigenesis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Dec 28;355(2):242-52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.08.035. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25218595
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester upregulates N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 via ERK pathway to inhibit human oral cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Sep;61(9). doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600842. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017. PMID: 28181403
-
MYH9 Facilitates Cell Invasion and Radioresistance in Head and Neck Cancer via Modulation of Cellular ROS Levels by Activating the MAPK-Nrf2-GCLC Pathway.Cells. 2022 Sep 13;11(18):2855. doi: 10.3390/cells11182855. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139430 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological targeting and the diverse functions of the metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, in cancer.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Sep;157:154-175. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.05.020. Epub 2019 May 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 31132412 Review.
-
The Oncogenic Signaling Disruptor, NDRG1: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Activity.Cells. 2021 Sep 10;10(9):2382. doi: 10.3390/cells10092382. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Ni(II)-Binding Activity of the Intrinsically Disordered Region of Human NDRG1, a Protein Involved in Cancer Development.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 9;12(9):1272. doi: 10.3390/biom12091272. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139110 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-630 Promotes Radioresistance by Induction of Anti-Apoptotic Effect via Nrf2-GPX2 Molecular Axis in Head-Neck Cancer.Cells. 2023 Dec 17;12(24):2853. doi: 10.3390/cells12242853. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132173 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Signature of Long Non-Coding RNA Associated with Areca Nut-Induced Head and Neck Cancer.Cells. 2023 Mar 11;12(6):873. doi: 10.3390/cells12060873. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980216 Free PMC article.
-
N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 can promote vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis in urothelial carcinoma.Virchows Arch. 2024 May;484(5):827-836. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03793-w. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 38561462 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA Profiling of Areca Nut-Induced Carcinogenesis in Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 3;16(21):3710. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213710. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meltzer C., Nguyen N.T., Zhang J., Aguilar J., Blatchins M.A., Quesenberry C.P., Jr., Wang Y., Sakoda L.C. Survival associated with consolidated multidisciplinary care in head and neck cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021;9:1945998211057852. doi: 10.1177/01945998211057852. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang J.T., Wang H.M., Chang K.W., Chen W.H., Wen M.C., Hsu Y.M., Yung B.Y., Chen I.H., Liao C.T., Hsieh L.L., et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC): Overexpression of NPM, CDK1 and NDRG1 and underexpression of CHES1. Int. J. Cancer. 2005;114:942–949. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20663. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lorini L., Ardighieri L., Bozzola A., Romani C., Bignotti E., Buglione M., Guerini A., Lombardi D., Deganello A., Tomasoni M., et al. Prognosis and management of recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2021;115:105213. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105213. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

