β-Arrestin2 Is Critically Involved in the Differential Regulation of Phosphosignaling Pathways by Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone and Taltirelin
- PMID: 35563779
- PMCID: PMC9103620
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091473
β-Arrestin2 Is Critically Involved in the Differential Regulation of Phosphosignaling Pathways by Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone and Taltirelin
Abstract
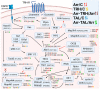
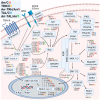
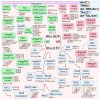
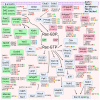
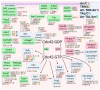
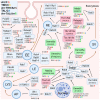
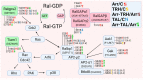
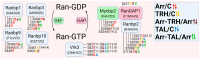
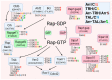
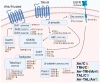
In recent years, thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and its analogs, including taltirelin (TAL), have demonstrated a range of effects on the central nervous system that represent potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of various neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases. However, the molecular mechanisms of their actions remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigated phosphosignaling dynamics in pituitary GH1 cells affected by TRH and TAL and the putative role of β-arrestin2 in mediating these effects. Our results revealed widespread alterations in many phosphosignaling pathways involving signal transduction via small GTPases, MAP kinases, Ser/Thr- and Tyr-protein kinases, Wnt/β-catenin, and members of the Hippo pathway. The differential TRH- or TAL-induced phosphorylation of numerous proteins suggests that these ligands exhibit some degree of biased agonism at the TRH receptor. The different phosphorylation patterns induced by TRH or TAL in β-arrestin2-deficient cells suggest that the β-arrestin2 scaffold is a key factor determining phosphorylation events after TRH receptor activation. Our results suggest that compounds that modulate kinase and phosphatase activity can be considered as additional adjuvants to enhance the potential therapeutic value of TRH or TAL.
Keywords: GH1 cells; TRH receptor; small GTPase-mediated signaling; taltirelin; thyrotropin-releasing hormone; β-arrestin2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of phosphosignaling pathways involved in transcription of cell cycle target genes by TRH receptor activation in GH1 cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115830. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115830. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37931515
-
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 (TRH-R1), not TRH-R2, primarily mediates taltirelin actions in the CNS of mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 May;38(6):950-6. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.256. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23303050 Free PMC article.
-
Taltirelin is a superagonist at the human thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Oct 9;3:120. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00120. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 23087672 Free PMC article.
-
Chemistry and biology of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and its analogs.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(26):2718-33. doi: 10.2174/092986708786242912. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18991632 Review.
-
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-immune system homeostatic hypothesis.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Jan;121(1):20-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Oct 21. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19000920 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and physiological insights into TRH receptor-mediated signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 6;10:981452. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.981452. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36147745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

