The Use of Molecular Dynamics Simulation Method to Quantitatively Evaluate the Affinity between HBV Antigen T Cell Epitope Peptides and HLA-A Molecules
- PMID: 35563019
- PMCID: PMC9105472
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094629
The Use of Molecular Dynamics Simulation Method to Quantitatively Evaluate the Affinity between HBV Antigen T Cell Epitope Peptides and HLA-A Molecules
Abstract
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV), a potentially life-threatening liver disease, makes people vulnerable to serious diseases such as cancer. T lymphocytes play a crucial role in clearing HBV virus, while the pathway depends on the strong binding of T cell epitope peptide and HLA. However, the experimental identification of HLA-restricted HBV antigenic peptides is extremely time-consuming. In this study, we provide a novel prediction strategy based on structure to assess the affinity between the HBV antigenic peptide and HLA molecule. We used residue scanning, peptide docking and molecular dynamics methods to obtain the molecular docking model of HBV peptide and HLA, and then adopted the MM-GBSA method to calculate the binding affinity of the HBV peptide-HLA complex. Overall, we collected 59 structures of HLA-A from Protein Data Bank, and finally obtained 352 numerical affinity results to figure out the optimal bind choice between the HLA-A molecules and 45 HBV T cell epitope peptides. The results were highly consistent with the qualitative affinity level determined by the competitive peptide binding assay, which confirmed that our affinity prediction process based on an HLA structure is accurate and also proved that the homologous modeling strategy for HLA-A molecules in this study was reliable. Hence, our work highlights an effective way by which to predict and screen for HLA-peptide binding that would improve the treatment of HBV infection.
Keywords: MM-GBSA; affinity; hepatitis B virus; molecular dynamics; residue scanning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
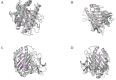
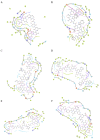
Similar articles
-
[Detection of antigen-epitope-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with hepatitis B virus infection by enzyme linked immunospot assay].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Aug;43(8):690-4. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20021848 Chinese.
-
Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes with peptides in vitro: identification of candidate T-cell epitopes in hepatitis B virus X antigen.J Immunother. 1999 Jul;22(4):279-87. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199907000-00001. J Immunother. 1999. PMID: 10404429
-
Discovery and Selection of Hepatitis B Virus-Derived T Cell Epitopes for Global Immunotherapy Based on Viral Indispensability, Conservation, and HLA-Binding Strength.J Virol. 2020 Mar 17;94(7):e01663-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01663-19. Print 2020 Mar 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31852786 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of T-cell epitopes in hepatitis B virus: identification, genotypic variation and relevance to antiviral therapeutics.Antivir Ther. 2008;13(2):161-75. Antivir Ther. 2008. PMID: 18505168 Review.
-
T cell recognition of hepatitis B and C viral antigens.Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Oct;24(10):641-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb01055.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994. PMID: 7531642 Review.
Cited by
-
A polymeric nanocarrier that eradicates breast cancer stem cells and delivers chemotherapeutic drugs.Biomater Res. 2023 Dec 15;27(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00465-9. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 38102651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guojin O.U., Wang J., Liu Z. Research progress on the correlation between HLA and HBV infection. Chin. J. Blood Transfus. 2018;31:1321–1326.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

