Integrated computational analysis reveals HOX genes cluster as oncogenic drivers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35562533
- PMCID: PMC9106698
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11590-1
Integrated computational analysis reveals HOX genes cluster as oncogenic drivers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
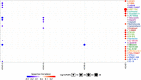
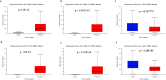
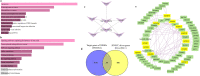
Alterations in homeobox (HOX) gene expression are involved in the progression of several cancer types including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, regulation of the entire HOX cluster in the pathophysiology of HNSCC is still elusive. By using different comprehensive databases, we have identified the significance of differentially expressed HOX genes (DEHGs) in stage stratification and HPV status in the cancer genome atlas (TCGA)-HNSCC datasets. The genetic and epigenetic alterations, druggable genes, their associated functional pathways and their possible association with cancer hallmarks were identified. We have performed extensive analysis to identify the target genes of DEHGs driving HNSCC. The differentially expressed HOX cluster-embedded microRNAs (DEHMs) in HNSCC and their association with HOX-target genes were evaluated to construct a regulatory network of the HOX cluster in HNSCC. Our analysis identified sixteen DEHGs in HNSCC and determined their importance in stage stratification and HPV infection. We found a total of 55 HNSCC driver genes that were identified as targets of DEHGs. The involvement of DEHGs and their targets in cancer-associated signaling mechanisms have confirmed their role in pathophysiology. Further, we found that their oncogenic nature could be targeted by using the novel and approved anti-neoplastic drugs in HNSCC. Construction of the regulatory network depicted the interaction between DEHGs, DEHMs and their targets genes in HNSCC. Hence, aberrantly expressed HOX cluster genes function in a coordinated manner to drive HNSCC. It could provide a broad perspective to carry out the experimental investigation, to understand the underlying oncogenic mechanism and allow the discovery of new clinical biomarkers for HNSCC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression profile in head and neck cancer: HOX-cluster embedded microRNA-196a and microRNA-10b dysregulation implicated in cell proliferation.BMC Cancer. 2013 Nov 9;13:533. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-533. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24209638 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the regulatory interactions between mutated genes and homeobox genes in the head and neck cancer progression.Arch Oral Biol. 2024 Mar;159:105872. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2023.105872. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Arch Oral Biol. 2024. PMID: 38147801
-
The role of HOX genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2016 Apr;45(4):239-47. doi: 10.1111/jop.12388. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016. PMID: 26661059 Review.
-
Identification of SERPINE1, PLAU and ACTA1 as biomarkers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on integrated bioinformatics analysis.Int J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep;24(9):1030-1041. doi: 10.1007/s10147-019-01435-9. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30937621 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SESN1, UHRF1BP1, and miR-377-3p as prognostic markers in mutated TP53 squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Oct 3;18(10):775-782. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1373212. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28886272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HOXA9 versus HOXB9; particular focus on their controversial role in tumor pathogenesis.J Appl Genet. 2024 Sep;65(3):473-492. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00868-x. Epub 2024 May 16. J Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38753266 Review.
-
Onco-Ontogeny of Squamous Cell Cancer of the First Pharyngeal Arch Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 16;25(18):9979. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189979. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

