Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: a multi-omics study with drug exploration
- PMID: 35551173
- PMCID: PMC9098425
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-00959-3
Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: a multi-omics study with drug exploration
Abstract
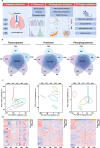
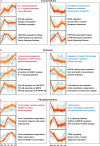
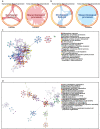
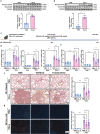
Silicosis is the most prevalent and fatal occupational disease with no effective therapeutics, and currently used drugs cannot reverse the disease progress. Worse still, there are still challenges to be addressed to fully decipher the intricated pathogenesis. Thus, specifying the essential mechanisms and targets in silicosis progression then exploring anti-silicosis pharmacuticals are desperately needed. In this work, multi-omics atlas was constructed to depict the pivotal abnormalities of silicosis and develop targeted agents. By utilizing an unbiased and time-resolved analysis of the transcriptome, proteome and phosphoproteome of a silicosis mouse model, we have verified the significant differences in transcript, protein, kinase activity and signaling pathway level during silicosis progression, in which the importance of essential biological processes such as macrophage activation, chemotaxis, immune cell recruitment and chronic inflammation were emphasized. Notably, the phosphorylation of EGFR (p-EGFR) and SYK (p-SYK) were identified as potential therapeutic targets in the progression of silicosis. To inhibit and validate these targets, we tested fostamatinib (targeting SYK) and Gefitinib (targeting EGFR), and both drugs effectively ameliorated pulmonary dysfunction and inhibited the progression of inflammation and fibrosis. Overall, our drug discovery with multi-omics approach provides novel and viable therapeutic strategies for the treatment of silicosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-omics study of silicosis reveals the potential therapeutic targets PGD2 and TXA2.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(5):2381-2394. doi: 10.7150/thno.47627. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33500731 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor fostamatinib limits tissue damage and fibrosis in a bleomycin-induced scleroderma mouse model.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;33(4 Suppl 91):S15-22. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26148346
-
Celastrol as a candidate drug for silicosis: From bioinformatics and network pharmacology to experimental validation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Dec;125(Pt B):111068. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111068. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37948856
-
Role of the Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Pathway in Driving Inflammation in IgA Nephropathy.Semin Nephrol. 2018 Sep;38(5):496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2018.05.019. Semin Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30177021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herbal compounds in the treatment of pulmonary silicosis.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 31;70(S3):S275-S287. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934817. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35099247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of EGFR attenuates EGF-induced activation of retinal pigment epithelium cell via EGFR/AKT signaling pathway.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 18;17(6):1018-1027. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.06.05. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38895677 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Integrated Multi-omics Analysis for Drug-Target Identification.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 14;14(6):692. doi: 10.3390/biom14060692. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reposition: Focalizing β-Alanine Metabolism and the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Its Metabolite Based on Multi-Omics Datasets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10252. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910252. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408583 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of omaveloxolone in counteracting muscle atrophy post-denervation: a multi-omics approach.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 2;22(1):991. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05810-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39487481 Free PMC article.
-
Stacking learning based on micro-CT radiomics for outcome prediction in the early-stage of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis model.Heliyon. 2024 May 6;10(9):e30651. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30651. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38765063 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

